


The unanswered questions The phrase unanswered questions or undeclared questions (Sanskrit avyākṛta, Pali: avyākata - "unfathomable, unexpounded"[1]), in Buddhism, refers to a set of common philosophical questions that Buddha refused to answer, according to Buddhist texts. The Pali texts give only ten, the Sanskrit texts fourteen questions. Fourteen questions[edit] According to their subject matter the questions can be grouped in four categories.[citation needed] Questions concerning the existence of the world in time 1. 2. ...or not? 3. ...or both? 4. ...or neither? (Pali texts omit "both" and "neither") Questions concerning the existence of the world in space 5. 6. ...or not? 7. ...or both? 8. ...or neither? Questions referring to personal identity 10. ...or is it different from the body? Questions referring to life after death 11. 12. ...or not? 13. ...or both? 14. ...or neither? Pali Canon[edit] Majjhima Nikaya 63 [2] & 72 [3] in the Pali canon contain a list of ten unanswered questions about certain views (ditthi):
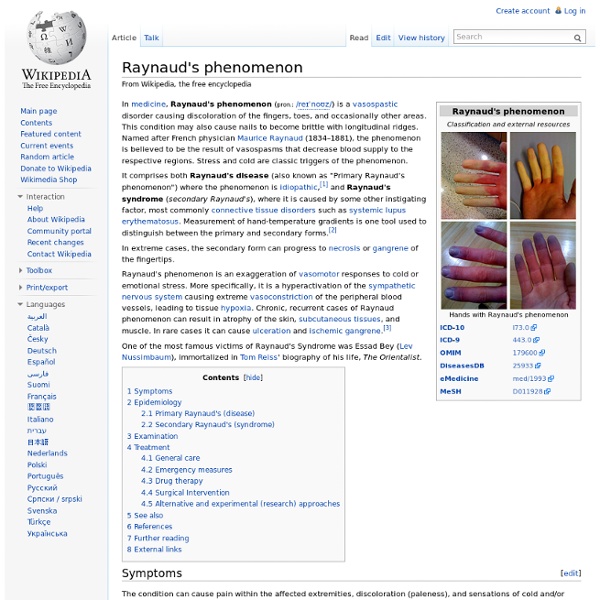
Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a median entrapment neuropathy that causes paresthesia, pain, numbness, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The pathophysiology is not completely understood but can be considered compression of the median nerve traveling through the carpal tunnel.[1] It appears to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.[2] Some of the predisposing factors include: diabetes, obesity, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, and heavy manual work or work with vibrating tools. There is, however, little clinical data to prove that lighter, repetitive tasks can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. Other disorders such as bursitis and tendinitis have been associated with repeated motions performed in the course of normal work or other activities.[3] Conservative treatments include use of night splints and corticosteroid injection. Signs and symptoms[edit] Untreated carpal tunnel syndrome
Overcome Social Anxiety with the 3-Second Rule Clouding of consciousness Heavy mist filling a valley. The metaphor of a cloud or fog is used to convey the idea of this disturbed mental state. Clouding of consciousness, also known as brain fog or mental fog,[1][2][3][4][5] is a term used in conventional medicine denoting an abnormality in the "regulation" of the "overall level"[6] of consciousness that is mild and less severe than a delirium. The sufferer experiences a subjective sensation of mental clouding described as feeling "foggy".[7] Background[edit] The term clouding of consciousness has always denoted the main pathogenetic feature of delirium since Greiner[8] first pioneered the term (Verdunkelung des Bewusstseins) in 1817.[9] The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) has historically used the term in its definition of delirium.[10] Recently the DSM has replaced “clouding” with “disturbance” but it is still the same thing. Psychopathology[edit] Alternative medicine[edit] See also[edit] References[edit]
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment Wheeler's delayed choice experiment is actually several thought experiments in quantum physics, proposed by John Archibald Wheeler, with the most prominent among them appearing in 1978 and 1984.[1] These experiments are attempts to decide whether light somehow "senses" the experimental apparatus in the double-slit experiment it will travel through and adjusts its behavior to fit by assuming the appropriate determinate state for it, or whether light remains in an indeterminate state, neither wave nor particle, and responds to the "questions" asked of it by responding in either a wave-consistent manner or a particle-consistent manner depending on the experimental arrangements that ask these "questions."[2] This line of experimentation proved very difficult to carry out when it was first conceived. Nevertheless, it has proven very valuable over the years since it has led researchers to provide "increasingly sophisticated demonstrations of the wave–particle duality of single quanta.
Patient Information Leaflets (PILs) - British Association of Dermatologists Alopecia is a general term for hair loss. Alopecia areata is a specific, common cause of hair loss that can occur at any age. It usually causes small, coin-sized, round patches of baldness on the scalp, although hair elsewhere such as the beard, eyebrows, eyelashes, body and limbs can be affected. In some people larger areas are affected and occasionally it can involve the whole scalp (alopecia totalis) or even the entire body and scalp (alopecia universalis). It is not possible to predict how much hair will be lost.
Scientists Are Beginning To Figure Out Why Conservatives Are…Conservative Scientists are using eye-tracking devices to detect automatic response differences between liberals and conservatives.University of Nebraska-Lincoln You could be forgiven for not having browsed yet through the latest issue of the journal Behavioral and Brain Sciences. If you care about politics, though, you'll find a punchline therein that is pretty extraordinary. Click here to read more from Mooney on the science of why people don't believe in science. Behavioral and Brain Sciences employs a rather unique practice called "Open Peer Commentary": An article of major significance is published, a large number of fellow scholars comment on it, and then the original author responds to all of them. That's a big deal. It is a "virtually inescapable conclusion" that the "cognitive-motivational styles of leftists and rightists are quite different." The authors go on to speculate that this ultimately reflects an evolutionary imperative. That's pretty extraordinary, when you think about it.
Mast Cells & Collagen Behaving Badly | My journey with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, M.E. & Mast Cell Disease 10 More Common Faults in Human Thought Humans This list is a follow up to Top 10 Common Faults in Human Thought. Thanks for everyone’s comments and feedback; you have inspired this second list! It is amazing that with all these biases, people are able to actually have a rational thought every now and then. There is no end to the mistakes we make when we process information, so here are 10 more common errors to be aware of. The confirmation bias is the tendency to look for or interpret information in a way that confirms beliefs. The Availability heuristic is gauging what is more likely based on vivid memories. Illusion of Control is the tendency for individuals to believe they can control or at least influence outcomes that they clearly have no influence on. Interesting Fact: when playing craps in a casino, people will throw the dice hard when they need a high number and soft when they need a low number. The Planning fallacy is the tendency to underestimate the time needed to complete tasks. Bonus Attribute Substitution
50,000 year old woman's toe reveals Neanderthals had sex with everyone According to an international team of anthropologists and geneticists at the University of California, Berkeley, our ancient Neanderthal cousins were a randy and apparently not very picky conglomerate of sexual deviants. Thanks to their remarkable research, in which DNA was extracted from a 50,000-year-old woman's toe, the team at Berkeley discovered Neanderthals had a long history of interbreeding among at least four different types of early humans living in Europe and Asia at the time. The team compared the Neanderthal genomes with those of modern humans and a recently recognised group of early humans called Denisovans, discovering that Neanderthals and Denisovans are very closely related, with their common ancestor splitting off from the ancestors of modern humans around 400,000 years ago. The research team estimates that between 1.5 and 2.1 percent of the genomes of modern non-Africans can be traced to Neanderthals.
Geology Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. In modern times, geology is commercially important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration / exploitation as well as for evaluating water resources. It is publicly important for the prediction and understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline. Geologic time[edit] Geological time put in a diagram called a geological clock, showing the relative lengths of the eons of the Earth's history. Important milestones[edit] Brief time scale[edit] Millions of Years Relative and absolute dating[edit] Geological events can be given a precise date at a point in time, or they can be related to other events that came before and after them. Relative dating[edit] Absolute dating[edit]