

Mankind. NASA. A Periodic Table of Visualization Methods. Geology. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates.
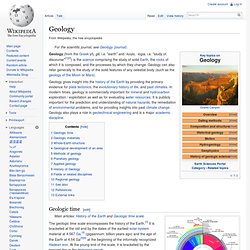
In modern times, geology is commercially important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration / exploitation as well as for evaluating water resources. It is publicly important for the prediction and understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline. Geologic time[edit] Geological time put in a diagram called a geological clock, showing the relative lengths of the eons of the Earth's history. Important milestones[edit] Brief time scale[edit] Everything is connected, remember? Progress.
10 More Common Faults in Human Thought. Humans This list is a follow up to Top 10 Common Faults in Human Thought.
Thanks for everyone’s comments and feedback; you have inspired this second list! Psychology & Experiment. Overcome Social Anxiety with the 3-Second Rule. Anxiety and Avoidance. THE BRAIN. Mnemonic memory.
Health. Manipulation en Français. To read & sort out. Worldwide Science. Astronomy & related... For the Love of Science, 18 behavioral.... Actualité de Karl Popper: "une vérité n'est scientifique que si. Homo sapiens - Who are we ? Conspiracy. La loi de cause à effet. 50,000 year old woman's toe reveals Neanderthals had sex with everyone.
According to an international team of anthropologists and geneticists at the University of California, Berkeley, our ancient Neanderthal cousins were a randy and apparently not very picky conglomerate of sexual deviants.
Thanks to their remarkable research, in which DNA was extracted from a 50,000-year-old woman's toe, the team at Berkeley discovered Neanderthals had a long history of interbreeding among at least four different types of early humans living in Europe and Asia at the time. The team compared the Neanderthal genomes with those of modern humans and a recently recognised group of early humans called Denisovans, discovering that Neanderthals and Denisovans are very closely related, with their common ancestor splitting off from the ancestors of modern humans around 400,000 years ago. The research team estimates that between 1.5 and 2.1 percent of the genomes of modern non-Africans can be traced to Neanderthals. Scientists Are Beginning To Figure Out Why Conservatives Are…Conservative.
Scientists are using eye-tracking devices to detect automatic response differences between liberals and conservatives.University of Nebraska-Lincoln You could be forgiven for not having browsed yet through the latest issue of the journal Behavioral and Brain Sciences.
If you care about politics, though, you'll find a punchline therein that is pretty extraordinary. Click here to read more from Mooney on the science of why people don't believe in science. Behavioral and Brain Sciences employs a rather unique practice called "Open Peer Commentary": An article of major significance is published, a large number of fellow scholars comment on it, and then the original author responds to all of them. The approach has many virtues, one of which being that it lets you see where a community of scholars and thinkers stand with respect to a controversial or provocative scientific idea. That's a big deal. Your Guide To Understanding Energy. Wheeler's delayed choice experiment. Wheeler's delayed choice experiment is actually several thought experiments in quantum physics, proposed by John Archibald Wheeler, with the most prominent among them appearing in 1978 and 1984.[1] These experiments are attempts to decide whether light somehow "senses" the experimental apparatus in the double-slit experiment it will travel through and adjusts its behavior to fit by assuming the appropriate determinate state for it, or whether light remains in an indeterminate state, neither wave nor particle, and responds to the "questions" asked of it by responding in either a wave-consistent manner or a particle-consistent manner depending on the experimental arrangements that ask these "questions.
"[2] This line of experimentation proved very difficult to carry out when it was first conceived. Nevertheless, it has proven very valuable over the years since it has led researchers to provide "increasingly sophisticated demonstrations of the wave–particle duality of single quanta. The most incredible thing you'll watch today is this video of sand. The unanswered questions. The phrase unanswered questions or undeclared questions (Sanskrit avyākṛta, Pali: avyākata - "unfathomable, unexpounded"[1]), in Buddhism, refers to a set of common philosophical questions that Buddha refused to answer, according to Buddhist texts.
The Pali texts give only ten, the Sanskrit texts fourteen questions. Fourteen questions[edit] According to their subject matter the questions can be grouped in four categories. [citation needed] Raynaud's phenomenon. In medicine, Raynaud's phenomenon /reɪˈnoʊz/ or Raynaud phenomenon is excessively reduced blood flow in response to cold or emotional stress, causing discoloration of the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas.
This condition may also cause nails to become brittle with longitudinal ridges. Named after French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the respective regions.