

Short-Term Gain. What Is a Short-Term Gain?
A short-term gain is a profit realized from the sale, transfer or other disposition of personal or investment property known as a capital asset that has been held for one year or less. A short-term capital gain occurs when an investment is sold that's been held for less than one year such as a stock. The gain is taxed as ordinary income, which is your income tax rate. Key Takeaways. Equity Long-Short. An equity long-short strategy is an investing strategy, used primarily by hedge funds, that involves taking long positions in stocks that are expected to increase in value and short positions in stocks that are expected to decrease in value.
You may know that taking a long position in a stock simply means buying it: If the stock increases in value, you will make money. On the other hand, taking a short position in a stock means borrowing a stock you don’t own (usually from your broker), selling it, then hoping it declines in value, at which time you can buy it back at a lower price than you paid for it and return the borrowed shares. Bond Market vs. Stock Market: What's the Difference? Bond Market vs.

Stock Market: An Overview It's time to invest your money. So where exactly are you going to do that? After you get your money together and decide on an investment strategy, it is time to buy some securities. The Differences Between Stocks and Futures. Financial Futures - Futures Fundamentals. An Overview Of Futures, Derivatives, and Liquidity. You are not alone if you believe futures and other derivatives increase volatility in the financial markets and were mostly responsible for the last decade's financial crisis.
Derivatives have been blamed for the financial collapse, but do they deserve the harsh judgment? Probably not. Instead, we need to understand them, how they are traded, their pros and cons, and how these instruments differ from each other. Equity Long-Short. Short-Term Gain. What is the difference between term structure and a yield curve? There is no difference between term structure and a yield curve; the yield curve is simply another name to describe the term structure of interest rates.
What Is the Term Structure of Interest Rates? The reason why the term structure of interest rates and a yield curve are the same is because the graph of the term structure of interest rates literally plots different yields being offered by bonds of different maturities. Futures Fundamentals - Derivatives Made Simple. Bank for International Settlements. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) is an international financial institution[2] owned by central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks".[3] The BIS carries out its work through its meetings, programmes and through the Basel Process – hosting international groups pursuing global financial stability and facilitating their interaction.
It also provides banking services, but only to central banks and other international organizations. It is based in Basel, Switzerland, with representative offices in Hong Kong and Mexico City. History[edit] BIS main building in Basel, Switzerland The BIS was established in 1930 by an intergovernmental agreement between Germany, Belgium, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, the United States, and Switzerland.[4][5] It opened its doors in Basel, Switzerland, on 17 May 1930. The BIS's original task of facilitating World War I reparation payments quickly became obsolete. Term Structure Of Interest Rates Definition. What is Term Structure Of Interest Rates?
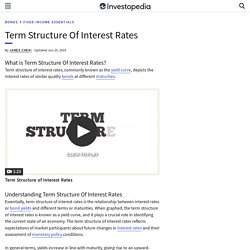
Term structure of interest rates, commonly known as the yield curve, depicts the interest rates of similar quality bonds at different maturities. Volume 75% Press shift question mark to access a list of keyboard shortcuts Play/PauseSPACE Increase Volume↑ Decrease Volume↓ Seek Forward→ Equity Derivative Definition. What is an Equity Derivative An equity derivative is a financial instrument whose value is based on equity movements of the underlying asset.
For example, a stock option is an equity derivative, because its value is based on the price movements of the underlying stock. Investors can use equity derivatives to hedge the risk associated with taking long or short positions in stocks, or they can use them to speculate on the price movements of the underlying asset. Basics of Equity Derivative Equity derivatives can act like an insurance policy. Equity derivatives can also be used for speculation purposes. Cash Settlement Definition. What is a Cash Settlement?
A cash settlement is a settlement method used in certain futures and options contracts where, upon expiration or exercise, the seller of the financial instrument does not deliver the actual (physical) underlying asset but instead transfers the associated cash position. For sellers not wishing to take actual possession of the underlying cash commodity, a cash settlement is a more convenient method of transacting futures and options contracts. Cash-settled contracts are one of the main reasons for the entry of speculators and, consequently, more liquidity in derivatives markets.
For example, the purchaser of a cash-settled cotton futures contract is required to pay the difference between the spot price of cotton and the futures price, rather than having to take ownership of physical bundles of cotton. What are Interest Rate Futures? - Corporate Finance Institute. Interest rate futures are futures contracts based on interest-bearingInterest Income financial instruments.

This futures contractFutures Contract can be cash-settled or it can involve the delivery of the underlying securitySecurity. Like other futures, this is an agreement for the long positionLong and Short Positions to receive the interest earned on a notional amount and the short positionLong and Short Positions to pay this amount. Financial Futures by FuturesTradingpedia.com. Financial Futures - Definition Financial Futures are futures contracts written on financial securities such as stocks, index and forex. Financial Futures - Introduction Financial Futures, also known as Futures on Financial Investments, are one of the most important innovations in the financial world today. Financial futures allow non-physical assets which cannot be traded on its own, such as an index, to become tradable for the purpose of hedging or speculation. Financial futures also provide leverage so that financial assets that are too expensive to trade the actual asset becomes accessible to traders with small fund size.
O Que é Hedge, Tipos e Como Investir Com Esse Instrumento. Guia Prático e Completo de Mercado Futuro. Offsetting Transaction Definition. What Is an Offsetting Transaction? An offsetting transaction cancels out the effects of another transaction. Offsetting transactions can occur in any market, but typically offsetting transactions refer to the options, futures, and exotic instrument markets.
An offsetting transaction can mean closing a transaction or taking another position in the opposite direction to cancel the effects of the first. Key Takeaways An offsetting transaction is an activity that cancels out the risks and benefits of another position or transaction.Offsetting can mean closing a position, if possible, but can also mean taking the opposite position in the same (or as close as possible) instrument.
Por que o Brasil Parou? Natália Cacioli & Yolanda Fordelone. Economia - Dívida pública sobe 21,7% em 2015, para R$ 2,79 trilhões, maior da série. Evolução da dívida pública Em R$ trilhões Fonte: Secretaria do Tesouro Nacional. Os pilares da economia - iNovOurém. Tomemos como exemplo o maior avião comercial do mundo: o A380 – um colosso que alberga nas suas asas quatro potentes motores que o impulsionam em direcção aos céus. «Economia é um avião com quatro motores em que dois vão a desacelerar» Entenda o que é déficit corrente, balanço de pagamentos e outros termos econômicos.
Mercado de Crédito. Mercado Monetário. Valor mobiliário. Origem: Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre. Tipos de títulos[editar | editar código-fonte] Mercado financeiro. Origem: Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre. Existem mercados gerais, onde muitos produtos são comercializados, e mercados especializados, onde apenas uma mercadoria é negociada. Os mercados funcionam colocando muitos compradores e vendedores interessados num "lugar", tornando assim mais fácil se encontrarem uns aos outros.