

Old versions of Windows, Mac and Linux Software, Apps & Abandonware Games - Download at OldVersion.com. How to Quickly Transfer Your Files and Settings to a New PC (or Mac) Three methods for transferring files to and from your Android tablet. If your Android tablet doesn't have a USB port, you can still easily transfer your files to and from a PC.
Jack Wallen explains three ways this can be done. Transferring files to and from your tablet can sometimes be difficult, especially if it doesn't include a standard USB port. Sure, emailing files back and forth works, but many users need to have a more consistent, reliable, and easier means to transfer files to and from their Android tablet. Conheça 10 atalhos de teclado indicados por especialistas. 10 fundamental differences between Linux and Windows. Before debating the relative merits and shortcomings of Linux and Windows, it helps to understand the real distinctions between them.
Jack Wallen has distilled the key differences into one list. Before debating the relative merits and shortcomings of Linux and Windows, it helps to understand the real distinctions between them. 10 fundamental differences between Linux and Windows. Visit alternate OSes with these five emulators. From DOS games to CoCo 2 to Commodore 64, these emulators will expand your platform horizons.
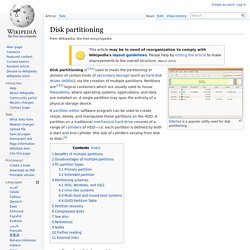
Disk partitioning. GParted is a popular utility used for disk partitioning Disk partitioning is[1][a] used to mean the partitioning or division of certain kinds of secondary storage (such as hard disk drives (HDDs)), via the creation of multiple partitions.
Partitions are[2][3] logical containers which are usually used to house filesystems, where operating systems, applications, and data are installed on. A single partition may span the entirety of a physical storage device. Benefits of multiple partitions[edit] Logical partitions require extended partitions. Master boot record.
This article is about a PC-specific type of boot sector on partitioned media.
For the first sector on non-partitioned media, see volume boot record. A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0. The MBR holds the information on how the logical partitions, containing file systems, are organized on that medium. How to Make Any Computer Boot Up or Shut Down on a Schedule.
Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux all allow you to schedule boot-ups, shut-downs, and wake-ups.
You can have your computer automatically power up in the morning and automatically shut down at night, if you’d like. This is less necessary than ever thanks to sleep mode — a typical laptop just enters low-power sleep mode it can quickly resume from when it’s not being used — but may still be useful for desktop PCs. Windows Windows allows you to set boot-up and shutdown times through the Task Scheduler. Scheduled tasks can run the “shutdown” command, shutting down your computer at a specific time. Shut Down: shutdown.exe -s -t 00Hibernate: rundll32.exe powrprof.dll,SetSuspendStateSleep: rundll32.exe powrprof.dll,SetSuspendState 0,1,0.
Determining the format of a file. Vigilância Extrema: descubra tudo o que os programas fazem em seu PC. Já ficou em dúvida se um programa que baixou estaria deixando o computador lento, acessando mais arquivos do que deveria ou simplesmente comprometendo a segurança do PC?
Sem os meios necessários para descobrir se isso realmente está acontecendo, nos resta apenas acreditar que o antivírus está realmente fazendo o serviço dele e que não há nada para nos preocuparmos. E o que você diria se soubesse que existe uma ferramenta prática para monitorar o que os programas fazem seu PC? 10 truques para se tornar um mestre em Dropbox. O Dropbox é uma ferramenta independente para sincronizar arquivos com a nuvem, e recentemente atingiu a marca de 100 milhões de usuários.
Ele é, sem dúvida, o serviço de armazenamento online mais popular que há, e por bons motivos. Why does Software Crash #1 – The Access Violation - Software Test Engineering @ Microsoft. Pop quiz: what does this line of code do when executed?
Int foo = (*((int*)0)); If you’re an astute reader, you can solve the answer just by reading the title of the blog post. But, more interestingly, let’s forget about that buzzword and analyze exactly what’s happening. The access violation is probably the most common crash in unmanaged software, so let’s break it down piece by piece to discover what’s happening. Sistema Operacional GNU. How to Restore Previous Versions of a File on Any Operating System. Every operating system backs up previous versions of files and offers an easy way to go back in time.

If you use a cloud storage service, it also keeps previous versions of your files. This is often useful when dealing with some sort of office document. But, any time you’ve modified any type of file and want to go back, it’ll work. Windows 7 On Windows 7, the Previous Versions feature allows you to restore older versions of your existing files. Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) defines the directory structure and directory contents in Unix[citation needed] and Unix-like operating systems, maintained by the Linux Foundation. The current version is 3.0, released on 18 May 2015.[1] Directory structure[edit]
GNU/Linux.