

Oxygen and Cancer - How cellular oxygenation kills cancerous cells. The link between oxygen and cancer is clear.

In fact, an underlying cause of cancer is usually low cellular oxygenation levels. In newly formed cells, low levels of oxygen damage respiration enzymes so that the cells cannot produce energy using oxygen. These cells can then turn cancerous because they don't make enough energy to function normally in the body. In 1931 Dr. Warburg won his first Nobel Prize for proving cancer is caused by a lack of oxygen respiration in cells. "Cancer, above all other diseases, has countless secondary causes. Poor oxygenation comes from a buildup of carcinogens and other toxins within and around cells, which blocks and then damages the cellular oxygen respiration mechanism. Warburg and other scientists found that the respiratory enzymes in cells, which make energy aerobically using oxygen, die when cellular oxygen levels drop below 65%.
When the mitochondrial enzymes get destroyed, they're host cell can no longer produce all its energy using oxygen. J. Chronic cellular hypoxia as the prime cause of cancer: what is the de-oxygenating role of adulterated and improper ratios of polyunsaturated fatty ... - PubMed - NCBI. Oxygen-Deprived RNA Molecules Lead to Tumor Progression. Reprogramming glucose metabolism in cancer: can it be exploited for cancer therapy? : Nature Reviews Cancer : Nature Research. Committed reactions in glucose metabolism.
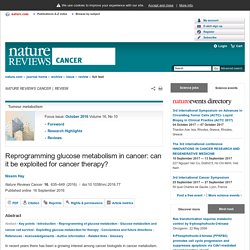
The canonical glycolysis pathway comprises several reversible enzymatic reactions and three irreversible reactions, which are known as the committed steps. The first committed step is catalysed by hexokinases that phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate (G6P). This reaction is perhaps the most important step in glucose metabolism — first, because it traps glucose inside cells, which could otherwise be exported by the glucose transporters, and second, because G6P is at the convergence point of not only glycolysis but also the PPP, the hexosamine pathway and glycogen synthesis (Figs 1, 2). Compared with normal cells (left), the flux of glucose metabolism and glycolysis is accelerated in cancer cells (right) by preferential expression of transporters and enzyme isoforms that drive glucose flux forward and to adapt to the anabolic demands of cancer cells.
Enzymes that catalyse the metabolic reactions are shown in ovals. v07p0817. Ein ganzheitlicher Ansatz, um den Krebs zu besiegen – NEXUS Magazin. Der ganzheitliche Ansatz zur Krebsbekämpfung kombiniert antimikrobielle und immunstimulierende Therapien mit Methoden zur Wiederherstellung des aeroben Energiestoffwechsels, der Entgiftung des Körpers und der Heilung von Gefühlszuständen.
Im Grunde kennen weder die Schulmedizin noch die alternative Medizin die Ursache von Krebs oder ein Heilmittel. In all den Jahrzehnten meiner Arbeit als Naturheilpraktiker und Autor zum Thema Gesundheit habe ich mich fortwährend um ein besseres Verständnis der tatsächlichen Vorgänge bemüht und bin überzeugt, dass die wichtigen Puzzleteile nunmehr ein sinnvolles Ganzes ergeben.
Dr.%20Otto%20Warburg%20Cancer%20Protocol Prime%20Cause%20of%20Cancer Encognitive. Leading to new selective targeting of cancer [Archive] - HER2 Support Group Forums. Attacking Cancer's Sweet Tooth Is Effective Strategy Against Tumors Mice Lacking Sugar-Metabolizing Pathway Outlive Four-Month Experiment [Harvard Medical School] BOSTON, MA-An ancient avenue for producing cellular energy, the glycolytic pathway, could provide a surprisingly rich target for anti-cancer therapies.
![leading to new selective targeting of cancer [Archive] - HER2 Support Group Forums](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/important-discovery-selective-131148962)
A team of Harvard Medical School (HMS) researchers knocked down one of the pathway's enzymes, LDHA, in a variety of fast-growing breast cancer cells, effectively shutting down glycolysis, and implanted the cells in mice. Control animals carrying tumor cells with an intact glycolytic pathway did not survive beyond 10 weeks. In striking contrast, only two of the LDHA-deficient mice died, one at 16 weeks, another at just over 18 weeks. Eighty percent of the mice outlived the four month experiment. The findings by Valeria Fantin, Julie St-Pierre, and Philip Leder appear in the June Cancer Cell. The mitochondria do display an intriguing difference, however. Therapeutic Implications for Targeted Therapy from the Resurgence of Warburg ‘Hypothesis’
Therapeutic Implications for Targeted Therapy from the Resurgence of Warburg ‘Hypothesis’ Writer and Curator: Larry H.
Bernstein, MD, FCAP (Note that each portion of the discussion is followed by a reference) It is now a time to pause after almost a century of a biological scientific discoveries that have transformed the practice of medicine and impacted the lives of several generations of young minds determined to probe the limits of our knowledge. In the century that we have entered into the scientific framework of medicine has brought together a difficult to grasp evolution of the emergence of human existence from wars, famine, droughts, storms, infectious diseases, and insect born pestilence with betterment of human lives, only unevenly divided among societal classes that have existed since time immemorial.
The conceptual challenge of cancer diagnosis and management has seemed insurmountable, but owes much to the post World War I activities of Otto Heinrich Warburg. John C. Multiple biological activities of lactic acid in cancer: influences on tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer generated lactic acid: Novel therapeutic approach. An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie. Regglyc. Wickramasekera_9_24_13. Is the Warburg Effect the Cause or the Effect of Cancer: A 21st Century View? A patient with glioblastoma multiforme who improved after taking citric acid orally.
J Gen Physiol 1927 Warburg 519 30. Science. J Cancer Res 1925 Warburg. Prime Cause and Prevention of Cancer - Cancer. 79d34fe7164d95daf0e041e94a738ac3. Insights and Ideas of Prof Peskin. J.yexmp.2010.08.