

11 Enchanting Mythological Figures Across Africa. Ailsa Johnson / © Culture Trip The vast African continent is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, each with their own beliefs and traditions.

With these varying beliefs comes a fascinating array of tales of wonder centred around mythological figures, which are etched into the cultures of the native people. Ancient West Africa: Bantu Migrations & the Stateless Society - Video & Lesson Transcript. Bantu - Overview. Definition, Characteristics, & Facts. Bantu languages, a group of some 500 languages belonging to the Bantoid subgroup of the Benue-Congo branch of the Niger-Congo language family.
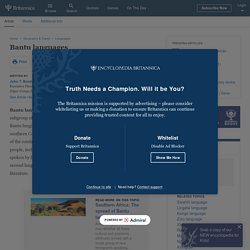
The Bantu languages are spoken in a very large area, including most of Africa from southern Cameroon eastward to Kenya and southward to the southernmost tip of the continent. Twelve Bantu languages are spoken by more than five million people, including Rundi, Rwanda, Shona, Xhosa, and Zulu. Swahili, which is spoken by five million people as a mother tongue and some 30 million as a second language, is a Bantu lingua franca important in both commerce and literature. Eastern Africa. The earliest written accounts of the East African coast occur in the Periplus Maris Erythraei—apparently written by a Greek merchant living in Egypt in the second half of the 1st century ce—and in Ptolemy’s Guide to Geography, the East African section of which, in its extant form, probably represents a compilation of geographic knowledge available at Byzantium about 400.
The Periplus describes in some detail the shore of what was to become northern Somalia. Ships sailed from there to western India to bring back cotton cloth, grain, oil, sugar, and ghee, while others moved down the Red Sea to the East African coast bringing cloaks, tunics, copper, and tin. Aromatic gums, tortoiseshell, ivory, and slaves were traded in return. Because of offshore islands, better landing places, and wetter climate, Arab traders from about 700 seem to have preferred the East African coast to the south of modern Somalia. There is little information concerning the period until the 8th century. Where Are The Bantu People Found In Africa? - WorldAtlas. The Bantu speaking peoples comprise of over 400 different ethnic groups found in many countries in Central, East and Southern Africa.

They are united by the Bantu language family and share many customs. There are between 440-680 distinct Bantu languages, comprising about 350 million speakers. Polynesian Mythology - Myth Encyclopedia - god, legend, war, world, creation, life, hero, people, children. Polynesia is a vast region of the Pacific Ocean consisting of many hundreds of widely separated, culturally and politically diverse island groups.
Ranging from Midway and Hawaii in the north to New Zealand in the south, the triangular area called Polynesia also includes Tahiti, Samoa, Tonga, Tuamotu, the Cook Islands, and the Pitcairn Islands. Although the mythology of Polynesia took different forms on various islands, many of the basic stories, themes, and deities were surprisingly similar throughout the region. Foundations of Religion and Myth. Australian Government Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Polynesian culture - Religion.
Polynesian belief systems emphasized animism, a perspective in which all things, animate and inanimate, were believed to be endowed to a greater or lesser degree with sacred supernatural power.
That power, known among Polynesians as mana, could be nullified by various human actions, and many of the region’s tapu (“prohibitions” or “taboos”) were intended to prevent such behaviours. As is typical of animist cultures, religious concerns permeated all aspects of life. Polynesian chiefs had great mana—so great, in fact, that in some societies, if a commoner touched the chief’s shadow, only that person’s death could compensate for the injury to the chief’s mana. In much of Polynesia it is still considered to be in very poor taste to step over a person’s legs, pass one’s hand over a person’s head, or stand with one’s head higher than that of a person of high rank, because these actions are believed to sap a person’s mana. Polynesian languages.
Polynesian languages, group of about 30 languages belonging to the Eastern, or Oceanic, branch of the Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian) language family and most closely related to the languages of Micronesia and Melanesia. Spoken by fewer than 1,000,000 persons spread across a large section of the Pacific Ocean, the Polynesian languages show a relative homogeneity, indicating that they have dispersed only in the last 2,500 years from an original centre in the Tonga-Samoa area. The best-known Polynesian languages are Samoan, with about 200,000 speakers; Maori, spoken in New Zealand by about 100,000 persons; Tahitian, with an unknown number of native speakers but widely used as a lingua franca in French Polynesia; and Hawaiian, with only a few remaining native speakers but formerly spoken by perhaps 100,000 persons.
Samoan is the national language of Samoa (formerly Western Samoa), and Tongan is the official tongue of the Kingdom of Tonga. Read More on This Topic. French Polynesia climate: average weather, temperature, precipitation, best time. In French Polynesia, a vast archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, the climate is tropical, influenced by the south-east trade winds, with a hot and humid season from November to April and a cooler season from May to October.
The hot season is also the rainiest, in addition, from December to April, there's the risk of cyclones (except on the Marquesas Islands). The temperatures vary little throughout the year, but they are high on the northern islands and gradually cooler as you move to the south. French Polynesia - Climate.
The climate is tropical—warm and humid.
A warm rainy season lasts from November to April, and a relatively cool dry season from May to October. The dispersion of the islands through 20° of latitude, however, results in regional climatic variation. Except in the Marquesas and the northern Tuamotus, precipitation is abundant, often falling in violent rain storms. 404. The Top 10 Polynesian Islands. There are over 10,000 Polynesian islands in the central and southern Pacific Ocean.

The region is generally defined by a triangle stretching from Hawaii in the north, to Easter Island in the east and New Zealand in the west. The main groups of Polynesian islands include the Cook Islands, French Polynesia, Samoa, Tonga, Tuvalu, and various others. Examples of Egyptian Myths: 8 Famous Ancient Stories. The ancient Egyptians really seemed to have it all.
They built the astonishing pyramids, crafted volumes of myths, and lived along the gorgeous, if not tempestuous, banks of the River Nile. As with any ancient culture, the Egyptians used mythology to try to explain the world around them. While some Eyptian myths explained nature's phenomena, others were told to make sense of the human condition - death and dying, love, deceit, and treachery. Regardless of their aim, myths are full of beautiful symbolism, often touting some virtue or human quality to aspire to. 8 Examples of Egyptian Mythology Stories. Egypt - Government and society. Egypt has operated under several constitutions, both as a monarchy and, after 1952, as a republic. The first and most liberal of these was the 1923 constitution, which was promulgated just after Britain declared Egypt’s independence. That document laid the political and cultural groundwork for modern Egypt, declaring it an independent sovereign Islamic state with Arabic as its language.
The vote was extended to all adult males. Egypt Religions - Demographics. Religions: Muslim (predominantly Sunni) 90%, Christian (majority Coptic Orthodox, other Christians include Armenian Apostolic, Catholic, Maronite, Orthodox, and Anglican) 10% (2015 est.) Definition: This entry is an ordered listing of religions by adherents starting with the largest group and sometimes includes the percent of total population. The core characteristics and beliefs of the world's major religions are described below. Baha'i - Founded by Mirza Husayn-Ali (known as Baha'u'llah) in Iran in 1852, Baha'i faith emphasizes monotheism and believes in one eternal transcendent God. Egypt - Languages. The official language of Egypt is Arabic, and most Egyptians speak one of several vernacular dialects of that language.
As is the case in other Arab countries, the spoken vernacular differs greatly from the literary language. Modern literary Arabic (often called Modern Standard Arabic or al-fuṣḥā, “clear” Arabic), which developed out of Classical, or medieval, Arabic, is learned only in school and is the lingua franca of educated persons throughout the Arab world.
What Language Is Spoken In Egypt? If you didn’t have the faintest clue as to what language is spoken in Egypt and you had to guess off the top of your head, you might be inclined to say “Arabic,” and you would be mostly correct. However, as with every other nation-state in existence, Egypt is composed of a complex fabric of demographics and immigrant influences. Additionally, it serves as a living reminder that spoken languages can vary drastically from their written standard versions, with the spoken languages more accurately reflecting regional differences and the written standard serving as a sort of official lingua franca that unifies the whole. Modern Standard Arabic. Egyptian Weather - AskAladdin. Geographic Regions of Egypt.