

PD Practice. El201209 takeaways. Glossary of Hattie's influences on student achievement - VISIBLE LEARNING. This Glossary explains influences related to student achievement published in John Hattie’s Visible Learning for teachers (Hattie 2012; 251ff).
You can find an older list of influences related to student achievement in Hattie (2009) Visible Learning. 1. Student Self-Reported Grades Self reported grades comes out at the top of all influences. Children are the most accurate when predicting how they will perform. Example for Self-reported grades: Before an exam, ask your class to write down what mark the student expects to achieve. Hattie cites five meta-studies: Educational Research: A Quick Guide. Top 10 Evidence Based Teaching Strategies. Most teachers care about their students’ results.

If you are reading this article, you are undoubtedly one of them. There is no doubt that teachers make a difference to how well their kids do at school. However, when you explore the thousands of research studies1 on the topic, it is apparent that some teaching strategies have far more impact than other teaching strategies do. Evidence Based Teaching Strategies Research shows that evidence based teaching strategies are likely to have the largest impact on student results. I wrote this article because you (and other teachers) have far too many demands on your time to sift through decades worth of research.
The Main Idea Visible Learning for Teachers April 2013. A Crash Course In EVIDENCE BASED TEACHING. Visible Learning. 00002182. McMaster LaPointe Effect Size Artical MERAFall2014. Rosenshine. The Top 10 Strategies Are ... An Objective Critique of Hatties Visible Learning Research. Teachers toolbox - Professor John Hattie's Table of Effect Sizes. Hattie says ‘effect sizes' are the best way of answering the question ‘what has the greatest influence on student learning?
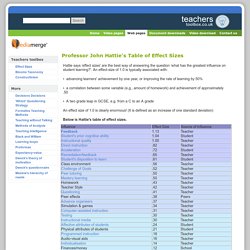
'. An effect-size of 1.0 is typically associated with: • advancing learners' achievement by one year, or improving the rate of learning by 50% • a correlation between some variable (e.g., amount of homework) and achievement of approximately .50 • A two grade leap in GCSE, e.g. from a C to an A grade An effect size of 1.0 is clearly enormous! Below is Hattie's table of effect sizes.
Terms used in the table (Interpreted by Geoff Petty) • An effect size of 0.5 is equivalent to a one grade leap at GCSE • An effect size of 1.0 is equivalent to a two grade leap at GCSE • ‘Number of effects is the number of effect sizes from well designed studies that have been averaged to produce the average effect size. • An effect size above 0.4 is above average for educational research Some effect sizes are ‘Russian Dolls' containing more than one strategy e.g.
Beware Over-interpretation! John Hattie's Eight Mind Frames For Teachers. “Hattie’s 8 Mind frames”.
Video scribe project by Cheryl Reynolds. In Visible Learning for Teachers (p. 159 ff) John Hattie claims that “the major argument in this book underlying powerful impacts in our schools relates to how we think! It is a set of mind frames that underpin our every action and decision in a school; it is a belief that we are evaluators, change agents, adaptive learning experts, seekers of feedback about our impact, engaged in dialogue and challenge, and developers of trust with all, and that we see opportunity in error, and are keen to spread the message about the power, fun, and impact that we have on learning.” John Hattie believes “that teachers and school leaders who develop these ways of thinking are more likely to have major impacts on student learning.”
During the summer holidays we stumbled upon a great video made by Cheryl Reynolds, a senior lecturer at the University of Huddersfield. Hattie effect size list - 195 Influences Related To Achievement John Hattie developed a way of synthesizing various influences in different meta-analyses according to their effect size (Cohen’s d). In his ground-breaking study “Visible Learning” he ranked 138 influences that are related to learning outcomes from very positive effects to very negative effects.
Hattie found that the average effect size of all the interventions he studied was 0.40. Therefore he decided to judge the success of influences relative to this ‘hinge point’, in order to find an answer to the question “What works best in education?” Originally, Hattie studied six areas that contribute to learning: the student, the home, the school, the curricula, the teacher, and teaching and learning approaches. (The updated list also includes the classroom.) Effective Teaching Strategies – High Desert Education Service District. “ Strategies for Effective Teaching are the instructional strategies that educators employ to significantly and quickly raise academic achievement in all subject areas.
In combination with the careful examination of student work and frequent collaboration among teachers, widespread implementation of these Power Strategies can produce dramatic results. Power Strategies for Effective Teaching synthesizes the work of many who have contributed to the field of educational research on instruction over the past 30 years.” Reeves Researchers at Mid-continent Research for Education and Learning (McREL) have identified nine instructional strategies that are most likely to improve student achievement across all content areas and across all grade levels. These strategies are explained in the book Classroom Instruction That Works by Robert Marzano, Debra Pickering, and Jane Pollock. 1. Resources: Danielson, C. 2007. Links: The Leadership and Learning Center The Marzano Research Center.