

Lewis Structures. A Sure-Fire Way to Draw Lewis Structures! · Head back to the helpdesk · Find more tutorials · Try some practice worksheets Lewis structures are a way to write chemical compounds where all the atoms and electrons are shown.

Sometimes, people have a lot of trouble learning how to do this. However, using the methods on this page, you should have very little trouble. The first method given allows you to draw Lewis structures for molecules with no charged atoms, while the second allows you to do it for charged molecules (such as polyatomic ions). How to draw Lewis structures for molecules that contain no charged atoms 1) Count the total valence electrons for the molecule: To do this, find the number of valence electrons for each atom in the molecule, and add them up. 2) Figure out how many octet electrons the molecule should have, using the octet rule: The octet rule tells us that all atoms want eight valence electrons (except for hydrogen, which wants only two), so they can be like the nearest noble gas.
Comments, questions, or gripes? Lewis Dot Structure Example - Octet Rule Exception. Lewis dot structures are useful to predict the geometry of a molecule.
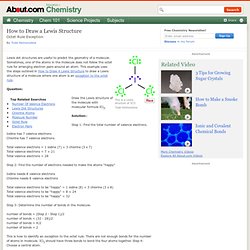
Sometimes, one of the atoms in the molecule does not follow the octet rule for arranging electron pairs around an atom. This example uses the steps outlined in How to Draw A Lewis Structure to draw a Lewis structure of a molecule where one atom is an exception to the octet rule. Question: Draw the Lewis structure of the molecule with molecular formula ICl3. Solution:: Step 1: Find the total number of valence electrons. Iodine has 7 valence electrons Chlorine has 7 valence electrons Total valence electrons = 1 iodine (7) + 3 chlorine (3 x 7) Total valence electrons = 7 + 21 Total valence electrons = 28 Step 2: Find the number of electrons needed to make the atoms "happy" Iodine needs 8 valence electrons Chlorine needs 8 valence electrons Total valence electrons to be "happy" = 1 iodine (8) + 3 chlorine (3 x 8) Total valence electrons to be "happy" = 8 + 24 Total valence electrons to be "happy" = 32.
Lewis Structures or Electron Dot Structures. Lewis Structures. Lewis Structures Writing Lewis Structures by Trial and Error The Lewis structure of a compound can be generated by trial and error.
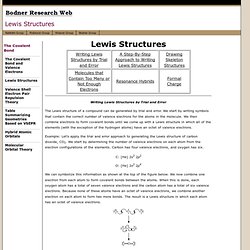
We start by writing symbols that contain the correct number of valence electrons for the atoms in the molecule. We then combine electrons to form covalent bonds until we come up with a Lewis structure in which all of the elements (with the exception of the hydrogen atoms) have an octet of valence electrons. Example: Let's apply the trial and error approach to generating the Lewis structure of carbon dioxide, CO2. C: [He] 2s2 2p2 O: [He] 2s2 2p4 We can symbolize this information as shown at the top of the figure below.
A Step-By-Step Approach To Writing Lewis Structures The trial-and-error method for writing Lewis structures can be time consuming. Step 1: Determine the total number of valence electrons. Step 2: Write the skeleton structure of the molecule. Step 3: Use two valence electrons to form each bond in the skeleton structure. ClO3-: 7 + 3(6) + 1 = 26. Rules for Lewis Structures.