

Horse skeletal anatomy. General horse anatomy. General horse anatomy. Horse muscle anatomy. Horse muscle anatomy. Horse skeletal anatomy. Heart Diagram, Eye Diagram, Dog Anatomy Diagram, Animal Anatomy Diagrams - AskMyVet.net. Dog Anatomy at Animal Corner. Dogs grow in various sizes and shapes.
The Greyhound is the ‘Fastest Dog on Earth’ and can run 45 miles per hour for short periods of time.The Irish Wolfhound is the largest dog standing 28 – 32 inches and weighing between 90 – 150 pounds. Irish Wolfhounds make excellent companions, however, their life expectancy is somewhat shorter than most dogs and is between 6 – 8 years.The Great Dane is the tallest dog standing 30 – 34 inches and weighing 120 – 200 pounds. These too have a short life expectancy and the average age is under 10 years although some can live 12 – 13 years. The Great Dane originates from Germany.The Chihuahua is the smallest dog standing at only 5 inches tall and weighing 2 – 6 pounds. Chihuahuas can live until they are 15 years old.The St.
Other breeds range in different sizes and weights between the above. Below is a diagram of a dogs anatomy: Their fur ranges from short, smooth fur to long shaggy fur to soft and fluffy to hard and coarse. Dogs have 42 teeth. Bothell Pet Hospital Case Studies. Rather than a specific case story this month, we thought it might be fun (and informative) to provide you all with a basic overview of your dog or cat’s anatomy.

What is anatomy? Anatomy is defined as the study of the structure of the body. Anatomy contributes to a pet’s basic appearance–from the way they walk, hold their heads, and wag their tails, to the way they chase a ball–all of which helps us recognize when something is wrong and may need attention. We as veterinarians study canine and feline anatomy to help us understand how the body works, and to appreciate the appearance of “normal” structures in order to identify abnormalities when they occur. You can imagine how important this knowledge is—both in the examination of your pet, and to help us make plans for treatment when needed. There are similarities… Although every dog and cat is a little different / has a few anatomical variations, they all have the same basic structure.
And differences… Communicating Location Like this: Related. Anatomy of the Dog and Cat. The pictures in this section are reprinted with permission by the copyright owner, Hill's Pet Nutrition, from the Atlas of Veterinary Clinical Anatomy.
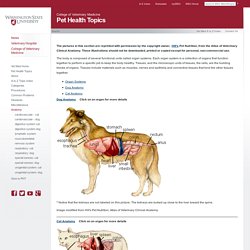
These illustrations should not be downloaded, printed or copied except for personal, non-commercial use. The body is composed of several functional units called organ systems. Each organ system is a collection of organs that function together to perform a specific job to keep the body healthy. Tissues, and the microscopic units of tissues, the cells, are the building blocks of organs. Tissues include materials such as muscles, nerves and epithelia and connective tissues that bind the other tissues together.
Dog Anatomy Click on an organ for more details * Notice that the kidneys are not labeled on this picture. Image modified from Hill's Pet Nutrition, Atlas of Veterinary Clinical Anatomy. Cat Anatomy Click on an organ for more details The organ systems include: 1. 2. 3.