

ASL Browser. Vol 11 No 2. La coordinación entre miembros del cuerpo. Faceta importante de la habilidad de motricidad gruesa. Share Mirar esta página en españolHomeJournal ContentsIssue ContentsVolume 11 Number 2©The Author(s) 2009 Interlimb Coordination: An Important Facet of Gross-Motor Ability Tatiana Bobbio State University of Campinas, Brazil Carl Gabbard & Priscila Caçola Texas A&M University Motor development attains landmark significance during early childhood.

Although early childhood educators may be familiar with the gross-motor skill category, the subcategory of interlimb coordination needs greater attention than it typically receives from teachers of young children. Early childhood researchers and educators are well aware of the importance of promoting motor skill function in young children. In addition to aiding professional evaluations of overall physical well-being, assessment is important for early detection of children with a high risk for developmental disorders.
Vol 11 No 2. La coordinación entre miembros del cuerpo. Faceta importante de la habilidad de motricidad gruesa. Teach kids locomotor skills - Health & Nutrition. By GreatSchools Staff Skipping isn’t just child's play, it’s crucial for development.
Sure, it’s never easy to keep exercising, but by starting early you could inspire a lifetime of movement. Locomotor skills are the basic ways to move, the building blocks of coordination. Help your child practice these important skills: walking, galloping, jumping, hopping, side-sliding, leaping and skipping. Start gradually with walking (the easiest) and steadily advance to skipping (the most difficult). This is a perfect transition activity, during a play date when things aren’t going well. A few tips to help children learn each locomotor skill: Walking: Use smooth, straight steps with arms swinging gently in opposition of feet. Development of Childhood Gross Motor Skills. Gross motor skills involve movement of the large muscles in arms, legs, and torso.
Gross motor activities include walking, running, skipping, jumping, throwing, climbing and many others. It may be easiest to think of “gross motor” skills as skills most utilized in a gym class or on a playground. Gross motor skills also include small movements of the large muscle groups. Gross Motor Skills. Gross Motor Skills Gross motor output entails the use of large muscles for participating in athletic events and accomplishing a range of other activities.
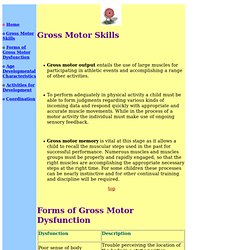
To perform adequately in physical activity a child must be able to form judgments regarding various kinds of incoming data and respond quickly with appropriate and accurate muscle movements. While in the process of a motor activity the individual must make use of ongoing sensory feedback. Gross motor memory is vital at this stage as it allows a child to recall the muscular steps used in the past for successful performance.
Adolescent Growth and Development. Authors as Published Erin Morgan, Research Associate, Human Development, Virginia Tech; Angela Huebner, Assistant Professor and Extension Specialist, Human Development, Virginia Tech Adolescence is a time of many transitions for both teens and their families.
To ensure that teens and adults navigate these transitions successfully, it is important for both to understand what is happening to the teen physically, cognitively, and socially; how these transitions affect teens; what adults can do; and what support resources are available. As you read the following information, keep in mind that while all teens develop, they don’t all follow the same timeline. I. What Is It? During the teen years, adolescents experience changes in their physical development at a rate of speed unparalleled since infancy.
Rapid gains in height and weight. How Do These Changes Affect Teens? Teens frequently sleep longer. What Can You Do? Don't criticize or compare the teens to others. II. III. Developmental Milestones: 4 to 5 Year Olds. Article Body.
NNCC Developmental Milestones. Developmental Milestones: 3 to 4 Year Olds. Article Body What are some of the developmental milestones my child should reach by three to four years of age?
With your child’s third birthday, the “terrible twos” are officially over and the “magic years” of three and four begin—a time when your child’s world will be dominated by fantasy and vivid imagination. During the next two years, he’ll mature in many areas. Here are some milestones to look for. NNCC Developmental Milestones. Resources - Pediatric Physical Therapy - Gross and Motor Skill Development.
Center for Pediatric Therapy - Gross Motor Developmental Milestones. Evaluation of Pediatric Development (Normal) Click for pdf: Milestonestable General Presentation Definition Developmental pediatrics is a subspecialty in pediatrics concerned with the study and treatment of the physical, social, emotional, and cognitive growth of children from birth through adolescence.

Why is it important? The concept of ongoing change and maturation is integral to the daily practice of pediatrics and encompasses all aspects of pediatric medicine. In general, how does development occur? The first 5 years of life are a period of extraordinary physical growth and increasing complexity of function. During the early preschool years (3-5 yrs), magical thinking blossoms and fantasy facilitates the development of role playing, sexual identity and emotional growth. Early adolescence (10-13 yrs) sees another period of rapid growth as the child approaches puberty.
Questions to Ask History After a general pediatric history, the developmental pediatric history usually focuses on developmental milestones. Physical exam References.