

Spinal fusion surgery to remain as Medicare billable item after surgeons lobby. Related Article Spinal surgeon Professor Ian Harris, who has published several studies critical of fusions, said the government's reversal showed that "doctors and surgeons have too much power, and the government is scared of them and happy to take the path of least resistance".
Spinal fusions are Australia’s fourth-most costly surgical procedure. Between 1997 and 2006, the number of private operations increased by 175 per cent. But evidence suggests one in five patients experiences a complication. Last year, following a recommendation from Choosing Wisely – the organisation that works to eliminate wasteful and unnecessary surgery – and with support from the chair of the government’s Medicare Benefits Schedule Review, the federal government announced plans to ban Medicare funding for the "treatment of uncomplicated axial chronic lower back pain". This is in line with British clinical guidelines that recommend against offering the procedure for lower back pain.
Large U.S. study goes against ‘common wisdom’ on need for heart procedures. People with severe but stable heart disease from clogged arteries may have less chest pain if they get a procedure to improve blood flow rather than just giving medicines a chance to help, but it won’t cut their risk of having a heart attack or dying over the following few years, a big U.S. federally-funded study found.
The results challenge medical dogma and call into question some of the most common practices in heart care. They are the strongest evidence yet that tens of thousands of costly stent procedures and bypass operations each year are unnecessary or premature for people with stable disease. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty A History of Procedure, Technology, Culture, Specialty, and Economics. To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription.
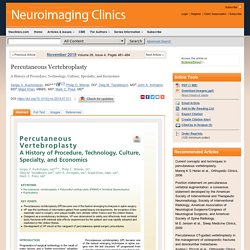
Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. Fig. 1 PMMA for malignant spinal lesions (1967). Wires encased by acrylic plastic (A) and anterior replacement of cervical vertebral bodies by acrylic plastic (B). Fig. 2. Operative versus non-operative treatment for 2-part proximal humerus fracture: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. - PubMed - NCBI.
Subacromial decompression surgery for adults with shoulder pain: a clinical practice guideline. - PubMed - NCBI. AF Ablation Update 2019. Five-Year Follow-up of Antibiotic Therapy for Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis in the APPAC Randomized Clinical Trial. - PubMed - NCBI. Seven in 8 children's tonsillectomies are unnecessary. A new study by the University of Birmingham has found that seven in every eight children who have their tonsils removed are unlikely to benefit from the operation.
Researchers analysed the electronic medical records of over 1.6 million children from more than 700 UK general practices dating between 2005 and 2016. They found that out of 18,271 children who had their tonsils removed during this time, only 2,144 (11.7 per cent) had enough sore throats to justify surgery. The researchers at the University's Institute of Applied Health Research concluded that their evidence, published today (Nov 6th) in British Journal of General Practice, showed that annually 32,500 children undergo needless tonsillectomies at a cost to the NHS of £36.9 million.
What's more, they found that many children who might benefit from having their tonsils removed are not having the surgical procedure. "Children may be more harmed than helped by a tonsillectomy. C-sections around the world have doubled in less than a generation. “Your baby is going to die.
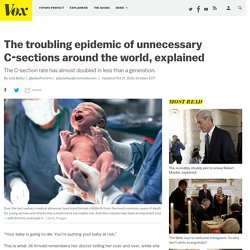
You’re putting your baby at risk.” This is what Jill Arnold remembers her doctor telling her over and over, while she was in labor in August 2005. Around 7 pm, Arnold started having regular contractions and was admitted to Kaiser Permanente in San Diego. A few weeks earlier, her doctor had recommended a planned cesarean section, which Arnold declined because she wasn’t convinced by her doctors’ reasoning. “I kept asking questions,” Arnold says, “and didn’t really think what they had to say” merited a C-section. New WHO guideline aims to reduce unnecessary c-sections. As the rate of cesarean sections increases worldwide, multifaceted clinical and nonclinical interventions that address clinicians’ and women’s beliefs and attitudes should be implemented to decrease unnecessary procedures, according to a series of papers published in The Lancet.

In one paper, Ties Boerma, PhD, director of the department of information, evidence and research at WHO, and colleagues found that in 2015, 29.7 million births occurred through cesarean section in the 169 countries that contribute to 98.4% of the world’s births, indicating two times as many births by this method since 2000. Subacromial decompression versus diagnostic arthroscopy for shoulder impingement: randomised, placebo surgery controlled clinical trial. - PubMed - NCBI.
Jamanetwork. Questions Are there long-term health risks after having adenoids or tonsils removed in childhood?
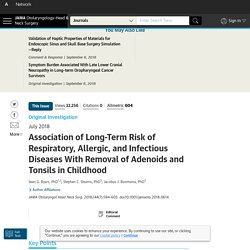
Findings In this population-based cohort study of almost 1.2 million children, removal of adenoids or tonsils in childhood was associated with significantly increased relative risk of later respiratory, allergic, and infectious diseases. Increases in long-term absolute disease risks were considerably larger than changes in risk for the disorders these surgeries aim to treat. Meaning The long-term risks of these surgeries deserve careful consideration.
Importance Surgical removal of adenoids and tonsils to treat obstructed breathing or recurrent middle-ear infections remain common pediatric procedures; however, little is known about their long-term health consequences despite the fact that these lymphatic organs play important roles in the development and function of the immune system. Most common shoulder operation is no more beneficial than placebo surgery: One of the most common surgical procedures in the Western world is probably unnecessary, suggests a new study. 1526571615 tfp212claviclefracturefv. Percutaneous coronary intervention in stable angina (ORBITA): a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. - PubMed - NCBI. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression for subacromial shoulder pain (CSAW): a multicentre, pragmatic, parallel group, placebo-controlled, three-gr... - PubMed - NCBI.
Jamanetwork. Question How does the proportion of the population undergoing computed tomography (CT) relate to the risk of nephrectomy?
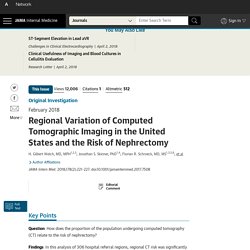
Findings In this analysis of 306 hospital referral regions, regional CT risk was significantly correlated with nephrectomy, and scanning an additional 1000 Medicare beneficiaries was associated with 4 additional nephrectomies. Beneficiaries residing in high-scanning regions face a higher risk of nephrectomy, presumably reflecting the incidental detection of kidney masses. Meaning Additional surgery should be considered one of the risks of excessive CT scanning. Importance While computed tomography (CT) represents a tremendous advance in diagnostic imaging, it also creates the problem of incidental detection—the identification of tumors unrelated to the clinical symptoms that initiate the test. Managing type-III acromioclavicular joint injuries. Between 2009 and 2016, WorkSafeBC accepted almost 1880 claims for acromioclavicular (AC) joint injuries.
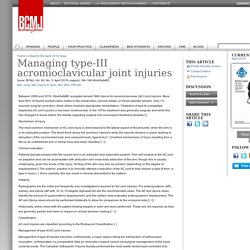
More than 80% of injured workers were males in the construction, service trades, or transit operator sectors. Only 1% required surgical correction, while others received appropriate rehabilitation. Surgery not always best option for women with abnormal cervical cancer test results. Can surgery lead to cognitive problems? QUESTION: I recently had knee-replacement surgery and I just don’t feel like myself.
I’m a retired school principal and I used to have an excellent memory. Now I struggle to remember the simplest things—even my husband’s name. I am slowly getting better, but it has been very frustrating and frightening. My doctor said I could be suffering a side effect from the anesthetic or the operation. Surgery In Old Age Can Hurt More Than Help : Shots - Health News. Maxine Stanich celebrated her 90th birthday with friends and family in 2010, more than two years after her implanted defibrillator was deactivated by Dr. Rita Redberg to comply with Stanich's "do not resuscitate" directive.
Courtesy of Susan Giaquinto/Kaiser Health News hide caption toggle caption Courtesy of Susan Giaquinto/Kaiser Health News Maxine Stanich celebrated her 90th birthday with friends and family in 2010, more than two years after her implanted defibrillator was deactivated by Dr. At 87, Maxine Stanich cared more about improving the quality of her life than prolonging it. She suffered from a long list of health problems, including heart failure and chronic lung disease that could leave her gasping for breath. Overuse of Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Since Gruentzig first used a balloon to inflate the left anterior descending of a young man with angina in 1977, there have been hundreds of millions of percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) done worldwide.
Most PCI are performed on patients who are asymptomatic or who have not had a trial of optimal medical therapy,1 which is equally effective in preventing myocardial infarction or death. Furthermore, in symptomatic patients there is no benefit to PCI in reducing symptoms or improving quality of life compared with a placebo procedure.2 This carefully performed analysis3 from the China PEACE study adds to the concern of overuse of PCI. It documents yet another commonly known but little discussed contributor to inappropriate PCI—the inaccuracy of angiographic readings.
Visual assessments tend to systematically overestimate the magnitude of the stenosis, meaning that patients will get an intervention on a lesion that is not hemodynamically significant. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression for subacromial shoulder pain (CSAW): a multicentre, pragmatic, parallel group, placebo-controlled, three-group, randomised surgical trial - The Lancet.
Bjsm.bmj. Overuse of Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Bjs. ‘Unbelievable’: Heart Stents Fail to Ease Chest Pain. Surgery of No Benefit for Meniscal Tears. Follow-up of Prostatectomy versus Observation for Early Prostate Cancer. - PubMed - NCBI. Breast Cancer Surgery: Less Is More. When surgery is just a stitch-up. What’s the difference between a homeopath and a surgeon? It’s a question that sounds like a joke, and it won’t have many surgeons laughing. Homeopathy is the scientifically implausible idea that diluted substances can somehow treat disease: it has never been shown to work and any effect is, at very best, a placebo effect. Effectiveness of Tympanostomy Tubes for Otitis Media: A Meta-analysis.
Comparison of Antibiotic Therapy and Appendectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Children: A Meta-analysis. Surgery Is One Hell Of A Placebo. The guy’s desperate. The pain in his knee has made it impossible to play basketball or walk down stairs. In search of a cure, he makes a journey to a healing place, where he’ll undergo a fasting rite, don ceremonial garb, ingest mind-altering substances and be anointed with liquids before a masked healer takes him through a physical ritual intended to vanquish his pain. Seen through different eyes, the process of modern surgery may look more more spiritual than scientific, said orthopedic surgeon Stuart Green, a professor at the University of California, Irvine. Our hypothetical patient is undergoing arthroscopic knee surgery, and the rituals he’ll participate in — fasting, wearing a hospital gown, undergoing anesthesia, having his surgical site prepared with an iodine solution, and giving himself over to a masked surgeon — foster an expectation that the procedure will provide relief, Green said.
Many operations more harmful than beneficial, top surgeon warns. Too many surgeons are performing operations that are likely to do more harm than good, a leading orthopaedic surgeon says. About half of orthopaedic surgical procedures have no scientific evidence from randomised trials proving they work better than non-operative treatment, Ian Harris told a meeting of 1900 surgeons this week. Research showed another 25 per cent are no better than non-surgical alternatives, he said. Yet many of these are still being performed. Professor Harris, of the University of NSW, said ineffective and potentially harmful operations included knee arthroscopy for arthritis, some forms of spinal surgery for low back pain, Achilles tendon repairs, some shoulder arthroscopic procedures, and wrist and ankle fracture fixations.
Despite many studies showing knee arthroscopy was not beneficial for almost all patients with arthritis, many medical guidelines continue to support the procedure for such people. "Surgeons think the operation is great," he said. Why Canada is wasting millions on useless knee surgeries - Health. An international expert panel says a common, minimally invasive surgery is largely useless for knee problems stemming from arthritis. The Urgent Need for Evidence in Arthroscopic Meniscal Surgery. Untitled. Prostate cancer patients report that surgery offers worst outcome on quality of life - Health. At the moment a man hears a diagnosis of prostate cancer, his first thought is often of survival. It's later — sometimes after treatment — that the patient considers the cost medical intervention can have on his sexual and mental well-being, said Prof.
Gabriela Ilie, who is conducting research on quality of life for prostate cancer patients. "At first the idea is, 'Do I want to survive, or do I want to have sexual function? '" the Dalhousie University scientist said. Controversial test could be leading to unnecessary open heart operations. Healthcare's perverse financial incentives - Frugal Nurse. A hospital puts profits over patient safety First do no harm. Why do surgeons continue to perform unnecessary surgery? Patient Safety in Surgery201711:1. Dogmas of modern medicine- The New Indian Express. Medicine is flying blind.
Thousands of medical journal articles are published every month on potential new treatments and diagnostic tests. Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy Decisions in a Population-Based Sample of Patients With Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Laparoscopic adhesiolysis was less beneficial than laparoscopy alone in the long term. Doctors perform thousands of unnecessary surgeries. Jonathan Stelly was playing baseball professionally, when he was told he needed a pacemaker. He stopped playing ball, but found out later he did not actually need the surgery that changed his life forever. Jonathan Stelly was 22, a semi-pro baseball player aiming for the big leagues, when a fainting spell sent him to his cardiologist for tests.
The doctor's office called afterward with shocking news: If Stelly wanted to live to age 30, he was told, he'd need a pacemaker. Spinal fusions serve as case study for debate over when certain surgeries are necessary. By some measures, Federico C. Vinas was a star surgeon. He performed three or four surgeries on a typical weekday at the Daytona Beach, Fla., hospital that employed him, and a review showed him to be nearly five times as busy as other neurosurgeons. Introducing decision aids at Group Health was linked to sharply lower hip and knee surgery rates and costs. Understanding regional variation in the use of surgery. To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. A Conceptual Framework for Appropriateness in Surgical Care:Reviewing Past Approaches and Looking Ahead to Patient-centered Shared Decision Making.
From the Center for Surgery and Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts (Z.C., A.M.B.); Department of Surgery, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts (Z.C.); Ariadne Labs, Boston, Massachusetts (Z.C.); Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts (P.S.); Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Francis Hospital and Medical Center, Providence, Rhode Island (S.K.A.); Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (M.D.N.); Department of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts (E.M.R., A.M.B.); and Department of Psychosocial Oncology and Palliative Care, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts (E.M.R.).
Why ‘Useless’ Surgery Is Still Popular. One surgeon says you need an operation. Another says you don't. Here's why that happens. Effect of PCI on Long-Term Survival in Patients with Stable Ischemic Heart Disease. Australians are undergoing unnecessary surgery – here’s what we can do about it. Repeated Upper Endoscopy in the Medicare Population: A Retrospective Analysis. Heart-attack-stent-angiogram-chest-pain-angina. A Sea Change in Treating Heart Attacks. 27 3 E.Rodriguez Borja et al. Utility of routine laboratory preoperative tests 030902 0. Measuring overtreatment: a structural model to estimate the impact of non-clinical factors on healthcare utilization. New Evidence That We Just Need To Give Women More Time To Labor. Large-for-Gestational-Age Ultrasound Diagnosis and Risk for... : Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Why Most Brazilian Women Get C-Sections - Olga Khazan. Read this before you get your knee replaced - Blog. Lumbar fusion no better than exercise and therapy in the long term. Arthroscopic surgery for knee pain. Association of hip pain with radiographic evidence of hip osteoarthritis: diagnostic test study. Most surgical meniscus repairs are unnecessary. Arthroscopic surgery for degenerative knee: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits and harms.
Treatment of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Study: Arthroscopic Knee Surgery No Better Than Sham Surgery. Orthopedists’ Financial Conflicts Can Hurt Patients, Surgeon Says. Surgery Versus Nonsurgical Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Randomized TrialSurgery Versus Nonsurgical Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. A randomized trial of epidural glucocorticoid injections for spinal stenosis. Preoperative Laboratory Investigations: Rates and Variability Prior to Low-risk Surgical Procedures. Why Many Doctors Don't Follow 'Best Practices' Less lung function testing before surgery? Wise Choice. Preoperative testing before low-risk surgical procedures. Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: The APPAC Randomized Clinical Trial. Treating Appendicitis Without Surgery. Antibiotics for Appendicitis: Penny wise but pound foolish.