

YouTube. History - Europe - Northern. Medieval Scandinavian History - Vikings in the Middle Ages. Though notorious for their fearsome Viking raids, Scandinavians were also farmers and craftsmen.
Find out more about this complex society that began in Norway, Sweden and Denmark and spread to Iceland, Greenland, Russia, much of Europe and even the Americas. Medieval Atlas: Maps of ScandinaviaAn index of maps depicting Scandinavia, in whole or in part. Germanic peoples. The Germanic peoples (also called Teutonic, Suebian or Gothic in older literature) are[1] an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic starting during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.[2] The term "Germanic" originated in classical times, when groups of tribes were referred to using this term by Roman authors.
For them, the term was not necessarily based upon language, but rather referred to tribal groups and alliances who were considered less civilized, and more physically hardened, than the Celtic Gauls living in the region of modern France. Tribes referred to as Germanic in that period lived generally to the north and east of the Gauls. Ethnonym Germanic The Latin ethnonym "Germani" seems to be attested in the Fasti Capitolini inscription for the year 222 BCE – de Galleis Insvbribvs et Germ(aneis) – where it may simply refer to "related" peoples, namely related to the Gauls. North Germanic languages. Ostrogoths. Ostrogoths. Visigoths. The eagles represented on these fibulae from the 6th century were a popular symbol among the Goths.
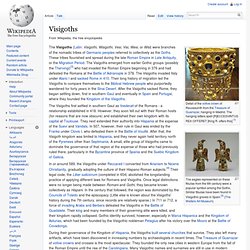
Similar fibulae have been found in Visigothic graves in Spain.[2] (The Walters Art Museum) The Visigoths first settled in southern Gaul as foederati of the Romans - a relationship established in 418. However, they soon fell out with their Roman hosts (for reasons that are now obscure) and established their own kingdom with its capital at Toulouse. Visigoths. GERMANIA: Visigoths, Ostrogoths, Vandals, Vikings, Orkney, etc. At first I wanted to erase the Roman name and convert all Roman territory into a Gothic Empire: I longed for Romania to become Gothia, and Athaulf to be what Caesar Augustus had been.

But long experience has taught me that the ungoverned wildness of the Goths will never submit to laws, and that without law, a state is not a state. The Germanic Tribes: Barbarians Against Rome (Episode 1) History of Sweden. Modern Sweden started out of the Kalmar Union formed in 1397 and by the unification of the country by King Gustav Vasa in the 16th century.
In the 17th century Sweden expanded its territories to form the Swedish empire. Most of these conquered territories had to be given up during the 18th century. In the early 19th century Finland and the remaining territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were lost. After its last war in 1814, Sweden entered into a personal union with Norway which lasted until 1905. Since 1814, Sweden has been at peace, adopting a non-aligned foreign policy in peacetime and neutrality in wartime.[1] Pre-historic age: 9,000 BC–AD 800[edit] History of Finland. The land area that now makes up Finland was probably settled immediately after the last ice age, which ended c. 9000 BC.
Most of the region was a part of the Kingdom of Sweden from the 13th century to 1809, when the vast majority of the Finnish-speaking areas of Sweden were ceded to the Russian Empire (excluding the Finnish-speaking areas of the modern-day Northern Sweden), making this area the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland. The Lutheran religion dominated. Finnish nationalism emerged, focused on Finnish cultural traditions, including music and—especially—the highly distinctive language and lyrics associated with it. The catastrophic Finnish famine of 1866–1868 was followed by eased economic regulations and extensive emigration. In the latter half of its independent history, Finland has maintained a mixed economy. Prehistory[edit] Paleolithic[edit] VIKINGS. The term Viking though used to denote ship-borne explorers, traders and warriors, is actually a verb describing the acts of the Danes who originated in Denmark and raided the coasts of the British Isles, France and other parts of Europe from the late 8th century to the 11th century.

This period of European history (generally dated to 793–1066) is often referred to as the Viking Age. It may also be used to denote the entire populations of these countries and their settlements elsewhere. Famed for their navigation ability and long ships, Vikings in a few hundred years colonized the coasts and rivers of Europe, the islands of Shetland, Orkney, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and for a short while also Newfoundland circa 1000 [1], while still reaching as far south as North Africa, east into Russia and to Constantinople for raiding and trading. Viking voyages grew less frequent with the introduction of Christianity to Scandinavia in the late 10th and 11th century. History of Norway. The history of Norway has been influenced to an extraordinary degree by the terrain and the climate of the region.
About 10,000 BC, following the retreat of the great inland ice sheets, the earliest inhabitants migrated north into the territory which is now Norway. They traveled steadily northwards along the coastal areas, warmed by the Gulf Stream, where life was more bearable. In order to survive they fished and hunted reindeer (and other prey). Between 5,000 BC and 4,000 BC the earliest agricultural settlements appeared around the Oslofjord. Gradually, between 1500 BC and 500 BC, these agricultural settlements spread into the southern areas of Norway - whilst the inhabitants of the northern regions continued to hunt and fish.
The Neolithic period started 4000 BC. Geats. History of Denmark.