

Study: Average Display Size Climbing On All Devices Except For Mobile PCs. A new study from NPD DisplaySearch today shows that on average, the diagonal size of LCD and other displays on electronic devices and public signboards is on the rise, with the notable exception of mobile PCs.
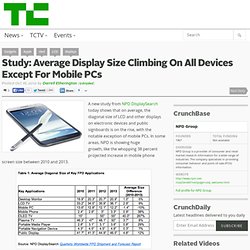
In some areas, NPD is showing huge growth, like the whopping 38 percent projected increase in mobile phone screen size between 2010 and 2013. Display sizes are also making modest increases in other areas, like the 5 percent change in desktop monitors (from 19.9-inches in 2010 to a projected 20.9-inches in 2013), or the 29 percent spike in portable media player size. Given that Apple has a huge portion of both the PMP and mobile phone spaces, its recent introduction of larger-screened iPhones, iPod touches and iPod nanos likely influenced the significant project growth in those areas.
Android and Windows Phone 8-powered devices are also seeing screen sizes packing on extra inches, however, so the fire was already started long before Apple came along to help bring up the average. Timeline. [return] 1946-1949 Timeline This section provides a chronological timeline of television-related events.

CBS gave the FCC a demonstration of their mechanical color system. Timeline Television - From Black and White to Color. 1831-1900 1901-1927 1928-1950 1951-present The Federal Radio Commission issues the first television station license (W3XK) to Charles Jenkins.
Vladimir Zworkin demonstrates the first practical electronic system for both the transmission and reception of images using his new kinescope tube. John Baird opens the first TV studio, however, the image quality was poor. Charles Jenkins broadcasts the first TV commercial. The BBC begins regular TV transmissions. Computer monitor. A monitor or a display is an electronic visual display for computers.
The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry and an enclosure. The display device in modern monitors is typically a thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) thin panel, while older monitors used a cathode ray tube (CRT) about as deep as the screen size. Originally, computer monitors were used for data processing while television receivers were used for entertainment. From the 1980s onwards, computers (and their monitors) have been used for both data processing and entertainment, while televisions have implemented some computer functionality. The common aspect ratio of televisions, and then computer monitors, has also changed from 4:3 to 16:9 (and 16:10). History[edit] Touchscreen. Interactive table, Ideen 2020 exposition, 2013.
HP Series 100 HP-150 ca. 1983, the earliest commercial touchscreen computer. The IBM Simon Personal Communicator, ca. 1993, the first touchscreen phone. Television. Televisions for consumer purchase First commercially available in a very crude form, on an experimental basis, in the late 1920s, then popularized in a greatly improved form shortly after World War II, the television set has become commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions, particularly as a vehicle for entertainment, advertising and news.
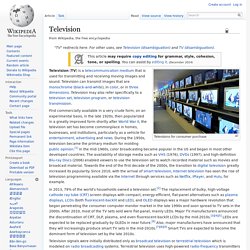
During the 1950s, television became the primary medium for molding public opinion.[1] In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting became popular in the US and began in most other developed countries. The availability of storage media such as VHS (1976), DVDs (1997), and high-definition Blu-ray Discs (2006) enabled viewers to use the television set to watch recorded material such as movies and broadcast material. Towards the end of the first decade of the 2000s, the transition to digital television greatly increased its popularity. Etymology The word television comes from Ancient Greek τῆλε (tèle), meaning "far", and Latin visio, meaning "sight".
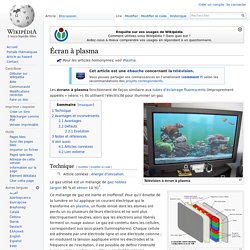
Écran à plasma. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Écran à cristaux liquides. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
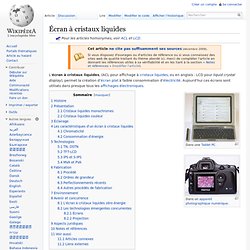
Pour les articles homonymes, voir ACL et LCD. L'écran à cristaux liquides, (ACL pour affichage à cristaux liquides, ou en anglais : LCD pour liquid crystal display), permet la création d’écran plat à faible consommation d'électricité. Aujourd'hui ces écrans sont utilisés dans presque tous les affichages électroniques.
Histoire[modifier | modifier le code] Les premiers panneaux d’affichage à cristaux liquides (LCD en anglais) ont été présentés en 1971[1], mais il faut attendre 1985 pour que Matsushita propose un écran plat d’une taille et d'une résolution suffisantes pour être utilisable sur des micro-ordinateurs. Les LCD sont utilisés depuis la fin des années 1990 en noir et blanc, puis en couleur depuis les débuts des années 2000 dans les téléphones portables, les ordinateurs personnels, les téléviseurs, les ordinateurs de bord pour les avions et les voitures. Présentation[modifier | modifier le code] Le principe de base est le même.
Tube cathodique. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
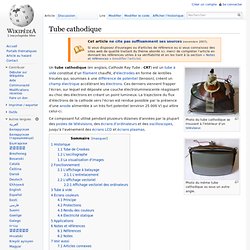
Photo du tube cathodique se trouvant à l’intérieur d’un téléviseur. Photo du même tube cathodique vu sous un autre angle. Ce composant fut utilisé pendant plusieurs dizaines d'années par la plupart des postes de télévisions, des écrans d’ordinateurs et des oscilloscopes, jusqu'à l'avènement des écrans LCD et écrans plasmas. The Evolution of Computer Monitors. Computer monitors are a crucial component of the modern world.

For many people, a solid computer monitor is their connection to much of their work and social life. But what a lot of people never stop to consider is that the computer monitor is an invention that has evolved considerably since its inception. Monitors have come a long way from their earliest incarnations. This has contributed to a much lower required level of user sophistication versus the early days. The Earliest Monitors and Interfaces.