

On this day: The fall of Singapore. BY 1942 SINGAPORE was one of the jewels in the crown of the British Empire.
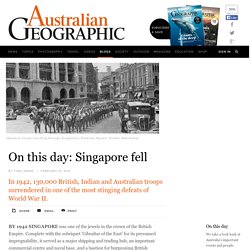
Complete with the sobriquet 'Gibraltar of the East' for its presumed impregnability, it served as a major shipping and trading hub, an important commercial centre and naval base, and a bastion for burgeoning British interests in South-East Asia. But after a disastrous campaign on the Malay Peninsula as the war in the Pacific got into full swing, overwhelmed British and Australian troops retreated there under the command of Lieutenant-General Arthur Percival and Australian Major-General Gordon Bennett, and with nowhere else to go, set up for a last stand. The British sent the newly built HMS Prince of Wales and the battle-hardened HMS Repulse to aid the defenders, but they were sunk by Japanese torpedo bombers before they could get there. Largest surrender in British war history The battle for Australia "POW stories are central to Australia's history in World War Two," Lachlan says. Remembering 1942: The fall of Singapore.
Dr Chris Coulthard-Clark Presented by Dr Chris Coulthard-Clark from the Memorial's Military History Section, on Friday 15 February 2002 beside the Roll of Honour at the Memorial. ( AWM PASU0169) Download the talk - 09:18 min (2.2Mb Mp3) Transcript.
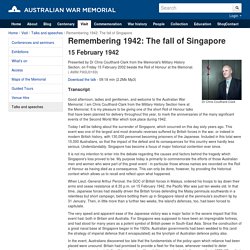
Fall of Singapore: Overview. Fall of Singapore view Australian positions in Singapore 8-15 February 1942.

By 31 January 1942, all British Empire forces had withdrawn from the Malay peninsula onto Singapore Island. Joseph Stalin - Facts & Summary. Joseph Stalin was born Josef Vissarionovich Djugashvili on December 18, 1878, or December 6, 1878, according to the Old Style Julian calendar (although he later invented a new birth date for himself: December 21, 1879), in the small town of Gori, Georgia, then part of the Russian empire.
When he was in his 30s, he took the name Stalin, from the Russian for “man of steel.” Stalin grew up poor and an only child. His father was a shoemaker and alcoholic who beat his son, and his mother was a laundress. As a boy, Stalin contracted smallpox, which left him with lifelong facial scars. Stalin's Role in the Second World War. In August 1939, Josef Stalin freed Hitler from his fear of the possibility of a war on two fronts by signing a pact of non-aggression with Germany.
As a result, a month later, Hitler invaded Poland and precipitated the Second World War. But, the security offered by the Brest-Litovsk treaty was short-lived. Hitler's rapid victories in the west made Stalin increasingly nervous. Adolf Hitler: Man of the Year, 1938. Greatest single news event of 1938 took place on September 29, when four statesmen met at the Führerhaus, in Munich, to redraw the map of Europe.
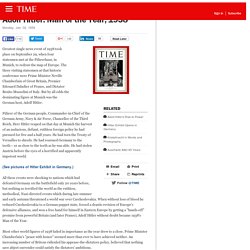
The three visiting statesmen at that historic conference were Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain of Great Britain, Premier Edouard Daladier of France, and Dictator Benito Mussolini of Italy. But by all odds the dominating figure at Munich was the German host, Adolf Hitler. Führer of the German people, Commander-in-Chief of the German Army, Navy & Air Force, Chancellor of the Third Reich, Herr Hitler reaped on that day at Munich the harvest of an audacious, defiant, ruthless foreign policy he had pursued for five and a half years. He had torn the Treaty of Versailles to shreds.
He had rearmed Germany to the teeth— or as close to the teeth as he was able. Most other world figures of 1938 faded in importance as the year drew to a close. Atomic Heritage Foundation. One of the greatest controversies to come out of World War II was whether the atomic bomb was necessary to bring about the war's end.
Supporters of the bombings generally believe that they prevented an invasion of the Japanese mainland, saving more lives than they took by doing so. Atomic Bomb. At approximately 8.15am on 6 August 1945 a US B-29 bomber dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese city of Hiroshima, instantly killing around 80,000 people.

Nazi Germany. The Nazi Regime in Germany. On January 5, 1919, two months after the conclusion of World War I and six months before the signing of the Peace Treaties at Versailles, the German Labour Party was brought into existence.
In September 1919, Adolf Hitler joined the political party and less than two years later the party's name was officially changed to National Sozialistische Deutsche Arbeiter Partei (NSDAP), thus beginning the infamous history of the Nazi regime in Germany. - Origins & Aims of the Nazi Party - Consolidation of Power - Measures of Rearmament - Common Plan Conspiracy & Aggressive War - Preparations for Aggression - The Planning of Aggression - Conferences of November 1937 & November 1939 The Origins & Aims of the Nazi Party. Adolf Hitler and The Holocaust. Causes and Motivations — United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Because the Holocaust involved people in different roles and situations living in countries across Europe over a period of time—from Nazi Germany in the 1930s to German-occupied Hungary in 1944—one broad explanation regarding motivation, for example, “antisemitism or “fear,” clearly cannot fit all.
In addition, usually a combination of motivations and pressures were in play. For the Holocaust as other periods of history, most scholars are wary of monocausal explanations. Interpretations of individuals’ motivations fall into two broad categories: first, cultural explanations (including ideology and antisemitism); and second, social-psychological ones (fear, opportunism, pressures to conform and the like). Antisemitism and Support for Nazism. 12 Things You Didn't Know about Women in the First World War. Roles for women in WWII. At first the government politely discouraged those women who wanted to perform some kind of military service. It soon became clear that the war was going to demand much more than the government had expected.
Women could do the technical jobs normally performed by men, freeing those men for combat. Each branch of the armed services formed their own auxiliary corps for women. These were not combat forces, as the government was determined that no female auxiliary forces would serve outside Australia. As the situation became more desperate, some women were called on to serve overseas, particularly in New Guinea. Before the war, it was generally expected that a working man was the main provider for his family.
Women also stepped into agricultural jobs. WW2 - The Blitz Hits London. Every so often, London’s landscape becomes drastically transformed – and it’s not always of Londoners’ choosing. Just like the Great Fire nearly 300 years before, the Blitz during World War II totally decimated parts of the capital. This time, however, it was no accident. By September 1940, London had already experienced German bombing. But the Blitz started in earnest on the afternoon of 7 September when the German Luftwaffe filled the skies in the first major daytime raid on London. Nearly 350 German bombers (escorted by over 600 fighters) dropped explosives on East London, targeting the docks in particular.
History - The Blitz (pictures, video, facts & news) Blitzkrieg. The classic characteristic of what is commonly known as "blitzkrieg" is a highly mobile form of infantry and armour, working in combined arms. (German armed forces, June 1942) Blitzkrieg (German, "lightning war" Despite its ubiquity in German and British journalism during World War II, Blitzkrieg was practically never used as official military terminology of the Wehrmacht during the war. Some senior officers, including Kurt Student, Franz Halder and Johann Adolf von Kielmansegg, even disputed the idea that it was a military concept.
Kielmansegg asserted that what many regarded as blitzkrieg was nothing more than "ad hoc solutions that simply popped out of the prevailing situation". History - World Wars: Blitzkrieg. The Turning Points In World War 2. December 1941, exhausted German soldiers surrender to winter-equipped Russian soldiers near Moscow The great strategic turning points in World War 2 , here is my list, explained : Great Britain and France declare war 1939 - In response to Hitler's invasion of Poland, Great Britain and France declared war on Germany. This surprised the over-confident Hitler and diverted his grand plan from its intended course by opening a second war front. Hitler's original plan was to occupy Poland, then Russia, and with Russia's endless natural resources in his control, to take the rest of the world while having one war front at a time.
Turning points of the Second World War. Monday 12 November 2012 by Emma Campbell. No commentsNews Now this is not the end. Causes of World War II. Some long-term causes of World War II are found in the conditions preceding World War I and seen as common for both World Wars. Supporters of this view paraphrase Clausewitz: World War II was a continuation of World War I by the same means. In fact, World Wars had been expected before Mussolini and Hitler came to power and Japan invaded China.[1] Causes of World War Two. The causes of World War Two can be divided into long term causes and short term causes. Australia's War 1939-1945. War time experiences, Australia and World War II, History, Year 9, NSW.
Second World War, 1939–45. On 3 September 1939 Prime Minister Robert Gordon Menzies announced the beginning of Australia's involvement in the Second World War on every national and commercial radio station in Australia. Almost a million Australians, both men and women, served in the Second World War. They fought in campaigns against Germany and Italy in Europe, the Mediterranean and North Africa, as well as against Japan in south-east Asia and other parts of the Pacific. The Australian mainland came under direct attack for the first time, as Japanese aircraft bombed towns in north-west Australia and Japanese midget submarines attacked Sydney harbour. Advancements in Technology in World War II. World War II for Kids: Technology. History >> World War 2 for Kids Technology played an important role in World War II.
Technology during World War II. Technology played a significant role in World War II. Facts, Summary, Combatants, & Causes.