

NHS uses AI scan to detect hidden heart disease. How hacking the human heart could replace pill popping - BBC Future. Covid: The man with 'super antibodies' Four causes for ‘Zoom fatigue’ and their solutions. Even as more people are logging onto popular video chat platforms to connect with colleagues, family and friends during the COVID-19 pandemic, Stanford researchers have a warning for you: Those video calls are likely tiring you out.

Professor Jeremy Bailenson examined the psychological consequences of spending hours per day on Zoom and other popular video chat platforms. (Image credit: Getty Images) Prompted by the recent boom in videoconferencing, communication Professor Jeremy Bailenson, founding director of the Stanford Virtual Human Interaction Lab (VHIL), examined the psychological consequences of spending hours per day on these platforms. Just as “Googling” is something akin to any web search, the term “Zooming” has become ubiquitous and a generic verb to replace videoconferencing. Can you boost your brain power naturally? - BBC Reel. Three human-like species lived side-by-side in ancient Africa. Scientists win historic Nobel chemistry prize for 'genetic scissors'
Image copyright Getty Images Two scientists have been awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing the tools to edit DNA.
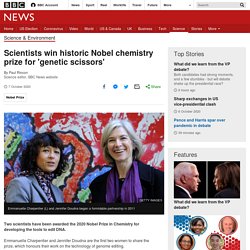
Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna are the first two women to share the prize, which honours their work on the technology of genome editing. Their discovery, known as Crispr-Cas9 "genetic scissors", is a way of making specific and precise changes to the DNA contained in living cells. The mystery of why some vaccines are doubly beneficial - BBC Future. The chilling experiment which created the first vaccine - BBC Future. Why you should read this out loud - BBC Future. Earth - How much of your body is your own?
This story is part of BBC Earth's "Best of 2016" list, our greatest hits of the year.
Browse the full list. • Bill Gates is actually worth $1,956• Canadian pop star Justin Bieber has five times fewer cells in his brain than in his liver• Top tennis player Serena Williams has 24.5 trillion red blood cells powering her body• Internet and social media pioneer Mark Zuckerberg’s body contains 800MB of data• President Barack Obama’s head rules his heart; his brain weighs 1.4kg, his heart just 0.4kg Welcome to The Making of Me and You, a unique, new digital interactive from BBC Earth that details extraordinary personalised facts. Just input your date of birth, sex at birth, height and weight, and choose the metric or imperial units that make most sense to you. Why Do People Stick Out and Bite Their Tongues When Concentrating? Jon K. asks: Why do I sometimes naturally bite my tongue when concentrating on things?

The short answer as to why some people bite their tongue when concentrating is that the tongue requires a surprising amount of brain power to manage- beyond general motor control, it’s covered in various types of sensors constantly providing feedback to your brain about what’s going on in your mouth and making sure your teeth aren’t mashing the tongue. Even when you’re not using it for speaking, it’s still continually moving slightly as it imperceptibly forms words you are thinking about. What's the point of having a nose? - BBC Reel. Big ideas reflecting our evolution and what makes us intrinsically human.
NeuroscienceThe quest to understand consciousnessCould lab-grown brains solve the mystery of consciousness? Watch now What's the point of noses? We explore the evolutionary purpose of noses.Now Playing What do our eyes say about us? Our eyeballs have evolved from a tiny, light-sensitive patch to the complex organs we have today.Watch now HumanityWas the Neolithic a big mistake? The strange idea that we are not in control of our minds - BBC Reel. The physics that suggests we have no free will - BBC Reel. What's the point of having free will? - BBC Reel. Computer inside the heart aims to aid treatment. BBC Radio 4 - Radio 4 in Four - Why it’s good to fidget.
Scientists discover powerful antibiotic using AI. Image copyright Getty Images In a world first, scientists have discovered a new type of antibiotic using artificial intelligence (AI).
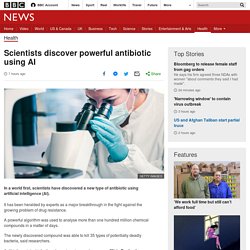
It has been heralded by experts as a major breakthrough in the fight against the growing problem of drug resistance. A powerful algorithm was used to analyse more than one hundred million chemical compounds in a matter of days. The newly discovered compound was able to kill 35 types of potentially deadly bacteria, said researchers. National Vital Statistics Reports 2017. AI 'outperforms' doctors diagnosing breast cancer. Image copyright Getty Images Artificial intelligence is more accurate than doctors in diagnosing breast cancer from mammograms, a study in the journal Nature suggests.
An international team, including researchers from Google Health and Imperial College London, designed and trained a computer model on X-ray images from nearly 29,000 women. The algorithm outperformed six radiologists in reading mammograms. AI was still as good as two doctors working together. Unlike humans, AI is tireless. 'Man on the Moon' moment - the year's big breakthroughs. It has been a remarkable year of promise in medical science - from inventing ways of treating the untreatable to reversing paralysis and keeping the brain alive after death.
Image copyright Fonds de dotation Clinatec "It was like [being the] first man on the Moon," said 30-year-old Thibault. China jails 'gene-edited babies' scientist for three years. Image copyright AFP A scientist in China who said he had created the world's first gene-edited babies has been jailed for three years.
He Jiankui was convicted of violating a government ban by carrying out his own experiments on human embryos, to try to give them protection against HIV. He was globally condemned when he announced his experiments, and the birth of twin babies, last November. Can you survive if you run out of air? - BBC Future. “Rapid cooling of the brain can increase survival time without oxygen,” says Tipton.
“If you reduce the temperature by 10 degrees the metabolic rate drops by a half to a third. If you lower the brain temperature down to 30C (86F), it can increase the survival time from 10 to 20 minutes. If you cool the brain to 20C (68F), you can get an hour.” The pressurised gas that saturation divers usually breathe may have given Lemons an additional chance. When breathing high levels of oxygen under pressure, it can dissolve into the blood stream, giving the body additional reserves to draw on.
Does birth order really matter? - BBC Ideas. Want to run faster? Improve your algorithm. Image copyright Reuters Runner Guillaume Adam wants to go faster, further and for longer. Like many modern runners, the former French national team member uses technology as a key element in helping him hit a new personal best. Gadgets are as essential a part of a runner's kit as the shoes on their feet. Few head out these days without a step counter, GPS watch, smartphone or smartwatch. The wearables keep an eye on the distance covered, pace, heart rate and cadence - helping to ensure they get as much out of the session as possible.
First drug that can slow Alzheimer's dementia. Image copyright Getty Images A US drug company says it has created the first therapy that could slow Alzheimer's disease, and it is now ready to bring it to market. Currently, there are no drugs that can do this - existing ones only help with symptoms. Biogen says it will soon seek regulatory approval in the US for the "groundbreaking" drug, called aducanumab. It plans to file the paperwork in early 2020 and has its sights on Europe too. Approval processes could take a year or two. The announcement is somewhat surprising because the company had discontinued work on the drug in March 2019, after disappointing trial results. But the company says a new analysis of a larger dataset of the same studies shows that higher doses of aducanumab can provide a significant benefit to patients with early Alzheimer's, slowing their clinical decline so they preserve more of their memory and every day living skills - things that the disease usually robs.
Dementia in football: Ex-players three and a half times more likely to die of condition - BBC Sport. How cells sense oxygen wins Nobel prize. Image copyright Getty Images Three scientists who discovered how cells sense and adapt to oxygen levels have won the 2019 Nobel Prize. Sir Peter Ratcliffe, of the University of Oxford and Francis Crick Institute, William Kaelin, of Harvard, and Gregg Semenza, of Johns Hopkins University share the physiology or medicine prize.
Their work is leading to new treatments for anaemia and even cancer. The role of oxygen-sensing is also being investigated in diseases from heart failure to chronic lung disease. Image copyright Albert and Mary Lasker Foundation. The Swedish Academy, which awards the prize, said: "The fundamental importance of oxygen has been understood for centuries but how cells adapt to changes in levels of oxygen has long been unknown. " Oxygen levels vary in the body, particularly: during exercise at high altitude after a wound disrupts the blood supply And when they drop, cells rapidly have to adapt their metabolism. Why aren't we living longer? Image copyright Yuri_Arcurs/Getty For the best part of two centuries people's life expectancy has been improving at a pretty rapid and consistent rate. In the 1840s people did not live much past 40 on average.
But then improvements in nutrition, hygiene, housing and sanitation during the Victorian period meant by the early 1900s life expectancy was approaching 60. Microneedle sensor aims to cut hospital superbugs. Image copyright Getty Images Seriously ill patients could get help to recover more quickly thanks to a sensor that uses tiny needles to monitor medication. The sensor can show how a patient has reacted to the type of antibiotic they have been given. Experts said the technique showed promise but needed more work to make it reliable enough to use in hospitals. Common cold stopped by experimental approach. 'There was no hope': Treatable disease often mistaken for Alzheimer's. Image copyright Barbara Gaal When John Searle started to fall down and lose his memory, he thought it was the early signs of dementia.
What is 'blobology' and how is it transforming biology? Image copyright UCSF CHIMERA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY. Kidney condition detected in minutes by app. A mobile phone app has speeded up the detection of a potentially fatal kidney condition in hospital patients. Staff describe the technology as a "potential lifesaver", providing diagnoses in minutes instead of hours. Acute kidney injury is caused by serious health conditions, including sepsis, and affects one in five people admitted to hospital. The condition is more common in older patients and, if not treated quickly, can affect other organs. Rory Cellan-Jones: 'My proton beam therapy diary' Anorexia stems from body as well as mind – study. The origins of the eating disorder anorexia nervosa are in both the mind and the body, according to an international study. Anorexia is seen as a serious psychiatric disease. Prosthetic limbs: An invention for amputees in the developing world. Why Ebola keeps coming back.
Image copyright Getty Images. The power of music: Vicky McClure's dementia choir. A million people in the UK are expected to be living with dementia by 2025. UAE woman wakes up after 27 years in a coma. Image copyright Science Photo Library. Parkinson's results beyond researchers' wildest dreams. ‘Three-person’ baby boy born in Greece. 'Tiniest baby boy' ever sent home leaves Tokyo hospital.
Exoskeleton helps people with paralysis to walk. Ibuprofen: Dr Stewart Adams who helped discover drug dies at 95. 'Virtual tumour' new way to see cancer. Zainab Mughal: Toddler with cancer spurs hunt for rare blood.