

Celtic Art: History, Characteristics. What Were the Main Characteristics of Hallstatt Arts and Crafts?
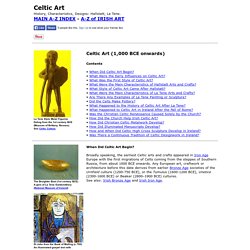
Hallstatt art from Central Europe is noted for its high quality iron tools and weaponry, along with its bronze-based manufacture of decorative items and ornamentation. But relatively few silver or Gold objects have been found from this era. Hallstatt was influenced by the militaristic Mycenean art and culture c.1650-1200 BCE which the Celts absorbed as they passed through the Black Sea area. The type-site in Austria, fully excavated by archeologists in the 19th century, included more than 2,000 graves packed with an assortment of functional and ornamental items. These and other Hallstatt-era hoards contained a mass of weaponry like axes, javelins, spears, cutting swords, daggers, helmets, bosses, shield plates.
Although it evolved and was influenced in several ways during its 300-year lifespan, the Hallstatt art style is typically very geometric. What Style of Celtic Art Came After Hallstatt? Celtic Culture: Characteristics of Visual Art, Language, Religion. Tribes of Continental Celts.
In Search of Ancient Ireland . Technology. By Carmel McCaffrey and Leo Eaton ometime in the fifth millennium B.C., new technology arrived in Ireland, carried by immigrants from Europe or native Irish who had learned new skills overseas.
This marked the beginning of Irish agriculture, the ability to grow cereal crops and raise livestock. Grain and farm animals arrived by boat since neither was native to Ireland. The Irish quickly improved on their scientific knowledge: By 3500 B.C., Neolithic farmers were raising great stone tombs for their dead, and the greatest of these were passage tombs, passages of dressed stone leading to a corbel-roofed central burial chamber covered by a mound of earth or stone as much as 40 feet high.
Many passage tombs were built on hilltops, towering over the surrounding countryside. Simon James's Ancient Celts page: introduction. Roman Republic Government's Three Branches. 3 Branches of Government in Republican Rome - Introduction: From the Founding of Rome in c. 753 B.C. to c. 509 B.C., Rome was a monarchy, ruled by kings.

Why Did Rome Fall? It's not entirely arbitrary that Medieval/Renaissance History at About.com begins and Ancient/Classical History ends in A.D. 476.
Edward Gibbon's 476 date for the Fall of Rome is conventionally acceptable because that's when the Germanic Odoacer deposed the last Roman emperor to rule the western part of the Roman Empire. However, the people who lived through the takeover would probably be surprised by the importance we place on this event. And there are other, reasonably momentous dates for the Fall of the Roman Empire. When Did Rome Fall? Some say the split into an eastern and western empire governed by separate emperors caused Rome to fall. Huge ancient Roman shipyard unearthed - Technology & science - Science - LiveScience. A large Roman shipyard has been uncovered an ancient port in Rome called Portus, researchers reported.
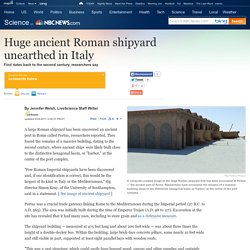
They found the remains of a massive building, dating to the second century, where ancient ships were likely built close to the distinctive hexagonal basin, or "harbor," at the center of the port complex. "Few Roman Imperial shipyards have been discovered and, if our identification is correct, this would be the largest of its kind in Italy or the Mediterranean," dig director Simon Keay, of the University of Southampton, said in a statement. [ See image of ancient shipyard ] Portus was a crucial trade gateway linking Rome to the Mediterranean during the Imperial period (27 B.C. to A.D. 565). The area was initially built during the time of Emperor Trajan (A.D. 98 to 117). Excavation at the site has revealed that it had many uses, including to store grain and as a defensive measure.
Ancient Rome - Ancient Rome from the Earliest Times Down to 476 A.D. Ancient Rome.

Chapter XLVI. Houses, Customs, Institutions, Etc. The private houses of the Romans were poor affairs until after the conquest of the East, when money began to pour into the city. Many houses of immense size were then erected, adorned with columns, paintings, statues, and costly works of art. Some of these houses are said to have cost as much as two million dollars. Military Technology: Using a Cloud of Dust in Ancient Warfare. In the present age of technology, imagining the role that such a simple element as dust played in ancient warfare can be difficult.
But what we regard as a mere nuisance often helped decide victory or defeat on the battlefields and during the military campaigns of the classical era. Ancient Rome's greatest defeat arrived in a cloud of dust. How the Romans Buried (or Cremated) Their Dead. Roman Army - Recruitment, Legions, Siege Warfare & More. Evolution of the Roman Army: Recruitment of Soliders for the Roman Army: The Roman army changed over time.

The consuls had the power to recruit troops, but in the last years of the Republic, provincial governors were replacing troops without the approval of the consuls. This led to legionaries loyal to their generals rather than Rome. Before Marius, recruitment was limited to citizens enrolled in the top 5 Roman classes. Rome's Ancient Catacombs. Aqueducts, Water Supply and Sewers in Ancient Rome. What We Think We Know About the Roman Water Supply: Ann Olga Koloski-Ostrow, a Brandeis classicist who has studied the Roman latrine, says, "There are no ancient sources where you can really learn about daily life....
You have to come upon information almost by chance. "[*] That means it's hard to answer all the questions or to say with any confidence that this bit of information about the bathroom habits of the Roman Empire applies to the Republic as well. With that caution, here is some of what we think we know about the water system of ancient Rome. Problems Stating Facts About Daily Life Roman Water Carriers - Aqueducts: The Romans are renowned for engineering marvels, among which is the aqueduct that carried water for many miles in order to provide a crowded urban population with relatively safe, potable water, as well as less essential but very Roman aquatic uses.
Tiber River. History - Ancient History in depth: The Fall of Rome. Julius Caesar and His Rise to Power in the Roman Republic. By the time of the First Triumvirate, the republican form of government in Rome was already on its way to monarchy. Before you get to the three men involved in the triumvirate, you need to know about some of the events and people that led to it: During the era of the late Republic, Rome suffered through a reign of terror. Terror's tool was a new one, the proscription list, by which large numbers of important, wealthy people, and often senators, were killed; their property, confiscated. Sulla, Roman dictator at the time, instigated this carnage: "Sulla now busied himself with slaughter, and murders without number or limit filled the city. Although when we think of dictators we think of men and women who want enduring power, a Roman dictator was: a legal official duly nominated by the Senate to handle a major problem, with a fixed, limited term.
Sulla's reign drained the Senate of power. Economic Reasons for the Fall of Rome. Whether you prefer to say Rome fell (in A.D. 410 when Rome was sacked or in 476 when Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustulus) or simply morphed into the Byzantine Empire and medieval feudalism, economic policies of the emperors had a heavy impact on the lives of the citizens of Rome. Primary Source Bias Although they say history is written by the victors, sometimes it's just written by the elites. This is the case with Tacitus (c. A.D.56-c.120) and Suetonius (c.71-c.135), our primary literary sources on the first dozen emperors. History - The Colosseum: Emblem of Rome. History: Vikings. Secrets of Lost Empires. By Dennis Gaffney Aqueducts are one of the wonders of the Roman Empire. These graceful structures are not only majestic, but are engineering marvels that survive to this day. In "Construct an Aqueduct," you are hired as Chief Water Engineer by the Roman Emperor.
Your job: to build an aqueduct that will supply the Roman city of Aqueductis with clean water to private homes, public baths and glorious fountains. Succeed, and citizens of Aqueductis will drink clean water and bathe happily. NOVA's Roman Aqueduct Manual Helpful hints for building your aqueduct Construct an Aqueduct Java applet (120k) To play the Java version of this game, you need a Java 1.1-enabled browser. A History of Ancient Rome.
Primary History - Romans. Camelot International: Britain's Heritage and History. Heritage > Medieval Life Religion in the Middle Ages Most people in medieval Europe were very religious. They took their babies to church to be christened and they were buried in the churchyard. Unlike today, the Catholic church was the only church in Europe and all christians belonged to it. With it's own laws, lands and taxes the Catholic church was a very powerful institution.
A History of Life Expectancy in the UK. We do not know exactly what average life expectancy at birth was in the past (before the 19th century we can only give rough estimates). History - British History in depth: Build an Arch Animation. The Ancient Olympics. Ancient Greece and You. Ancient Greek calculating device continues to reveal secrets. (PhysOrg.com) -- It's known as the Antikythera mechanism, a metal gear driven device found over a century ago on a sunken Roman ship, near the island of Antikythera, that for just as many years has had scientists analyzing, scratching their heads and offering suggestions as to its purpose. Some have called the device the first analog computer; others the first mechanical computing device.
Either way, the device very clearly demonstrates that the Greeks of 150 to 100 BCE knew far more about gears and calculating machines than had been thought possible just a decade or so ago. Wright has even built (completed in 2006) what he believes to be an almost exact replica of the device. Error loading skin: Invalid XML. Classics Technology Center: Connections between Ancient Greek Theater and Religion.
Connections between Ancient Greek Theater and Religion by Peter Baiter, Betty Banks & John Burke. What the Ancients Knew: Coliseum's Elevators. Ancient Greek ships traded more than just wine. (PhysOrg.com) -- While many historians have assumed that Greek sailors were using amphorae, or ancient storage containers, to transport and trade wine, new DNA testing is providing evidence that these containers were used for many different products. Death, Burial, and the Afterlife in Ancient Greece.
Theater in Ancient Greece. Ancient Greece : Athenian Democracy. Greek Archeologist Discovers Odysseus’s Palace In Ithaca. Ancient Greece - Information on Ancient Greece. Greek Pottery. Early Bronze Age Greek Pottery (c.3,000 - 2,000 BCE) The Greek Chorus in Greek Dramas. About the Greek Philosopher. Name: Aristocles [don't confuse the name with Aristotle], but known as PlatoPlace of Birth: AthensDates 428/427 - 347 B.C.Occupation: Philosopher. Everyday Life in Ancient Greece, 4th Century BC. Everyday Life in Ancient Greece Centered within a loose collection of city-states (often at war with one another), ancient Greek culture reached its pinnacle during the fourth century BC - an era described as its "Golden Age.
" Architecture in Ancient Greece. Pericles (Leader of Athens) Biography. Geography of Ancient Greece. Primary History - Ancient Greeks. Profile of the Greek God Apollo. Individual Sporting Events or Games of the Ancient Olympics. Unique Marvel of Ancient Greek Technology Gives Up New Secrets. 3 Important Aspects About Daily Life in Ancient Greece. Ancient Greece.