

What reinforcement and punishment are to parents? Using Reinforcement and Punishment at Home. The Use of Reinforcement and Punishment in Shaping a Child's Behavior. Skinner’s Operant Conditioning: Reinforcements & Punishments. Reinforcement & Punishment. The Difference between Positive/Negative Reinforcement and Positive/Negative Punishment. February 5, 2013 7:40 pm Published by Kelley Prince M.A., BCBA In Applied Behavior Analysis, there are two types of reinforcement and punishment: positive and negative.
It can be difficult to distinguish between the four of these. Therefore, the purpose of this blog is to explain the differences in order to help parents and professionals develop appropriate interventions to improve behavior. What Is the Difference Between Reinforcement and Punishment? In a perfect world, you wouldn't need to worry about discipline, but all parents face situations that require intervention.

The goal of discipline is to decrease the undesirable behaviors and increase the positive choices your child makes. Learning: Negative Reinforcement vs. Punishment. Untitled. Understanding the Differences Between Positive and Negative Reinforcement. Parents often use both reinforcement and punishment as tools to modify their children's behavior or to help when working to improve their developmental skills, like sensory processing or fine motor skills.
The main purpose of both negative and positive reinforcement is to boost the rate of specific behavior, but they have various differences and similarities. When you introduce the "reinforcement" concept to someone, they become encouraged or motivated to perform a repetitive behavior, which is either: To avoid any unwanted stimulus.To reward again or receive the wanted reinforcer. Positive and Negative Reinforcement. If you prefer watching instead. What is Negative Reinforcement? Negative Reinforcement: What Is It and How Does It Work? What is negative reinforcement?

Negative reinforcement is a method that can be used to help teach specific behaviors. With negative reinforcement, something uncomfortable or otherwise unpleasant is taken away in response to a stimulus. Over time, the target behavior should increase with the expectation that the unpleasant thing will be taken away. Read on to learn more about this type of learning. Examples of negative reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement in Psychology (Definition + 5 Examples) If you read our earlier piece on positive punishment, you know that there are different methods of teaching and instilling good habits and behaviors.
One of the most powerful and effective methods is one that you’re probably at least somewhat familiar with: positive reinforcement. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our 3 Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values and self-compassion and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students or employees. You can download the free PDF here. Positive Reinforcement for Adolescents. By the time children have reached adolescence, their responses are often ingrained, but parental actions can still positively affect adolescent behavior.
Since adolescents are struggling to develop their personal identity and are concerned about their body image, parental support is crucial to help positively frame experiences as learning opportunities. Positive reinforcement remains a powerful teaching tool during these formative years, and we encourage parents to take time to contemplate the ways they can help adolescents mature and become self-reliant.
Reinforce mature decisions by allowing increased privileges when adolescent demonstrates increased responsibility. For instance, an adolescent who consistently demonstrates the ability to come home at the requested time might be allowed a later curfew - whereas an adolescent who has not completed requested chores will not be allowed to leave home that evening.Express pleasure at positive adolescent behavior. Positive Reinforcement in Teenagers. Teenagers might need special incentives to learn skills, develop responsibility and make positive decisions about their conduct.

One effective way to encourage the behaviors you want is to use the behavior management technique of positive reinforcement. Through positive reinforcement, you gradually make it more likely that your teenager will demonstrate the desired behaviors. Goals of Positive Reinforcement The beauty of positive reinforcement is that it teaches and motivates specific behaviors by using items or activities that appeal to your teenager, states Shannon Baranski, psychology professor with the Houston Community College. Types of Punishment.
Guidelines for using punishment. Positive vs Negative Punishment - Psychestudy. Punishment is a fundamental concept of Operant Conditioning, whose major objective is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior from occurring again.
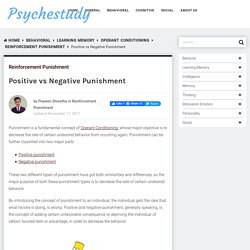
Punishment can be further classified into two major parts These two different types of punishment have got both similarities and differences, as the major purpose of both these punishment types is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior. By introducing the concept of punishment to an individual, the individual gets the idea that what he/she is doing, is wrong.
Positive and negative punishment, generally speaking, is the concept of adding certain unfavorable consequence or depriving the individual of certain favored item or advantage, in order to decrease the behavior. Difference between Positive and Negative Punishment. Positive and Negative Punishment. How Negative Punishment Works. Negative punishment is an important concept in B.

F. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning. In behavioral psychology, the goal of punishment is to decrease unwanted behavior. In the case of negative punishment, it involves taking something good or desirable away to reduce the occurrence of a particular behavior. One of the easiest ways to remember this concept is to note that in behavioral terms, positive means adding something while negative means taking something away. Negative Punishment. Negative punishment is a popular concept in parenting.
We'll explain what it is and how you can implement it with eight real examples. Your child is acting out, and it seems like nothing you say or do will curb their exasperating behavior. Sound familiar? No matter whether you're a parent, a babysitter, a nanny, or a day care worker, we’ve all been there -- scratching our heads, desperately racking our brains for the right solution to get our children to play nice. And with so many different parenting techniques out there, it's hard to figure out which one will work best for your child. Negative Punishment. Positive Punishment: What It Is, Benefits, and Examples. Positive punishment is a form of behavior modification. In this case, the word “positive” doesn’t refer to something pleasant. Positive punishment is adding something to the mix that will result in an unpleasant consequence.
The goal is to decrease the likelihood that the unwanted behavior will happen again in the future. This approach may be effective in certain circumstance, but it’s only one part of the equation. Guiding your child toward alternative behaviors that are more appropriate to the situation are also needed. Effects of Positive Punishment Techniques.
If you have ever done potty training for a toddler, behavior training for a dog, or even had cheat meals while dieting, you have engaged in a technique called operant conditioning. It involves learning and altering certain behaviors by utilizing reinforcement and punishment. If you are teaching a dog to not pull on the leash while walking, you might reinforce good behavior where you give them a treat when they do not pull. If you are teaching a toddler not throw temper tantrums when they do not get their way, you might put them in timeout when they act out. If you are trying to lose weight, you might reward yourself for having a good week of working out and eating well by having pizza for dinner on the weekend.
All these examples involve altering behaviors with the intention of seeking more desirable behaviors (i.e. a dog that does not a pull on the leash, a toddler that does not throw a tantrum every time the parent says ‘no’, a person that develops better exercise and eating habits). Positive Punishment. Positive punishment is the practice of adding a punishment and can be contrasted to negative punishment, which is the process of taking away something pleasant. Timeouts and extra chores are examples of positive punishment. Although spanking may be a form of discipline, the American Academy of Pediatrics advises against spanking children. Positive punishment can be an effective component of a parent's disciplinary repertoire. 7 Ways To Discipline Your Child. Video: Tips on disciplining a teenager. Discipline for Teens: Strategies and Challenges.
When your child becomes a teenager, your parenting role is likely to shift. You may find yourself becoming more of a guide, rather than an enforcer. That’s not to say your child won’t need you to intervene when there are safety issues or that your teen won’t need consequences. But, by now, it’s OK to let your child make some choices on their own, even when you think it’s a bad choice. Typical Teen Behavior Teens like to test the limits of their independence.1 So don’t be surprised when your teen argues with you when you say no, or when they go behind your back to do as they please. Adolescence can be a tumultuous time for teens as they change physically, emotionally, and socially. Meanwhile, as friends and romantic relationships grow increasingly important, your teen will want to spend more time with their peers. Your teen also will want more privacy. When Should You Take the Phone Away from a Teenager? Kate Gosselin, the mom in the reality series Kate Plus 8, isn’t exactly someone we’d turn to for inspirational parenting.
But she recently said something on a television special that caught our attention. Discipline strategies for teenagers. Teenage discipline: the basics. Effective Vs. Counterproductive Methods Of Teen Punishment. Updated September 17, 2018 Reviewer Tiffany Howard, LPC, LCADC Source: pinterest.com In the current day and age, parental knowledge regarding effective and counterproductive methods of setting limits and consequences for their teens is paramount. However, a clear understanding is often easier said than obtained. Teenagers are infamous for unruliness and difficulty, thus breeding stress for parents who have countless other responsibilities aside from their children..
Punishment Rules for Difficult Teenagers. Teenagers are notoriously hard to deal with, especially when it comes to responsibility and discipline. Walking the fine line between childhood and adulthood, most teens struggle to assert their own free will, resulting in rebellion against their parents. Catch 'em being good! My cousin Barbara bought me milkshakes. Starting in first grade, for every 6-week report card that was all "A's," she took me to the local Dairy Treet in our small south Texas town and treated me to a chocolate milkshake. Physical, cognitive, and socioemotional changes. Can You Discipline Your Child Without Using Punishment? – Psychology Benefits Society. This is the third in a series of weekly blog posts addressing discipline and parenting practices. In this series we will explore the reasons that parents choose among discipline approaches, the science behind those techniques, and alternative approaches to discipline.
By Alan E. Kazdin, PhD, ABPP (Yale University) Article 1.1: Is This Typical Teenage Behavior or a Warning Sign of Mental Illness? Some rebellious, irritable, or anxious behavior is a normal and healthy part of being a teenager. However, when shifts in a teenager’s personality are more extreme, they may be indicators of a mental health issue. Teenagers: 20 tips for good behaviour. 1. Parents Play an Important Role in Shaping Adolescent’s Behavior. Parents Play an Important Role in Shaping Adolescent’s Behavior. Stages of Adolescence. A Parent's Guide to Surviving the Teen Years. Parents, family relationships & teenagers.