Physical, cognitive, and socioemotional changes
What is adolescence? Adolescence is the period of transition between childhood and adulthood. Children who are entering adolescence are going through many changes (physical, intellectual, personality and social developmental). Adolescence begins at puberty, which now occurs earlier, on average, than in the past.
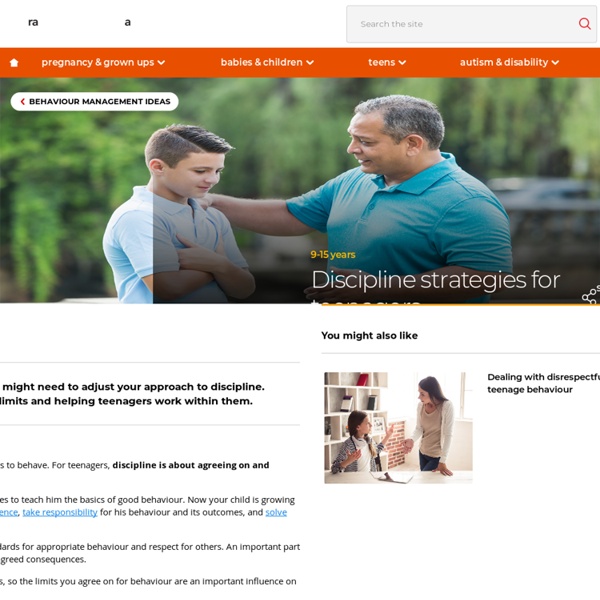
Discipline for Teens: Strategies and Challenges
When your child becomes a teenager, your parenting role is likely to shift. You may find yourself becoming more of a guide, rather than an enforcer. That’s not to say your child won’t need you to intervene when there are safety issues or that your teen won’t need consequences.
Dealing with Disrespectful Teenage Behaviour
Disrespectful or rude behaviour in teenagers is something many parents face at some point. Here are some strategies that can help you manage this kind of behaviour in the meantime. Sometimes you might feel that interactions with your child all seem a bit like this: You – “How’s that book project going?”
Positive Reinforcement in Teenagers
Teenagers might need special incentives to learn skills, develop responsibility and make positive decisions about their conduct. One effective way to encourage the behaviors you want is to use the behavior management technique of positive reinforcement. Through positive reinforcement, you gradually make it more likely that your teenager will demonstrate the desired behaviors. Goals of Positive Reinforcement
The Difference Between Punishment and Discipline
When it comes to correcting your child's misbehavior, there’s a big difference between punishment and discipline. While punishment focuses on making a child suffer for breaking the rules, discipline is about teaching him how to make a better choice next time. What Is Punishment?
Parenting Quiz - Active Parenting
Differences in parenting styles are a problem for both parents and children. At the least, it invites kids to play one parent against the other in a smart attempt to get the answer that they want to hear. This is not the child’s fault. After all, a child is just using good common sense! However, it does create a situation in which rules are not clear or consistently enforced, which is bad for the child as well as for the parent. At its extreme, a polarization of styles can occur in which one parent compensates for the perceived weaknesses of the other.
What Is the Difference Between Reinforcement and Punishment?
In a perfect world, you wouldn't need to worry about discipline, but all parents face situations that require intervention. The goal of discipline is to decrease the undesirable behaviors and increase the positive choices your child makes. Both reinforcement and punishment are ways to achieve that goal, but the methods have subtle differences that may make one better suited for your child.
Positive and Negative Consequences
When most parents think about consequences for kids, they usually envision negative consequences, like a time-out or taking away a video game. While negative consequences are instrumental in changing a child's behavior, positive consequences are also effective discipline tools. When used together, positive and negative consequences will change your child's behavior1 —as long as they are used consistently.
Tips for Communicating With Your Teen
The teenage years have a lot in common with the terrible twos. During both stages our kids are doing exciting new things, but they’re also pushing boundaries (and buttons) and throwing tantrums. The major developmental task facing both age groups is also the same: kids must pull away from parents and begin to assert their own independence. No wonder they sometimes act as if they think they’re the center of the universe.
Understanding the Differences Between Positive and Negative Reinforcement
Parents often use both reinforcement and punishment as tools to modify their children's behavior or to help when working to improve their developmental skills, like sensory processing or fine motor skills. The main purpose of both negative and positive reinforcement is to boost the rate of specific behavior, but they have various differences and similarities. When you introduce the "reinforcement" concept to someone, they become encouraged or motivated to perform a repetitive behavior, which is either:
Negative Punishment Examples and Scenarios
Nobody ever wants their stuff taken away. That is the main concept behind negative punishment. Using negative punishment example scenarios, gain an understanding of the concept and its effectiveness. Then, go on to explore the difference between positive and negative punishment. Exploring Negative Punishment
A Parent's Guide to Surviving the Teen Years
You've lived through 2 a.m. feedings, toddler temper tantrums, and the back-to-school blues. So why is the word "teenager" causing you so much worry? When you consider that the teen years are a period of intense growth, not only physically but emotionally and intellectually, it's understandable that it's a time of confusion and upheaval for many families.
How Negative Punishment Works
Negative punishment is an important concept in B. F. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning. In behavioral psychology, the goal of punishment is to decrease unwanted behavior. In the case of negative punishment, it involves taking something good or desirable away to reduce the occurrence of a particular behavior.
Negative Punishment Drawbacks – Tired Mom Supermom
Negative Punishment Drawbacks Inside this post: The drawbacks of using negative punishment when disciplining children. It’s shocking how many adults still use negative punishment with their kids today. I see comments such as “just give them a spank, that’ll stop the whining” in response to my how to stop whining in children article, which uses positive parenting to solve the whining issue.