

Duel of the Sun and Moon by Isaia on DeviantArt. ADLIVUN - the Inuit legendary place (Inuit mythology) The spirits who live there are also called the Adlivun.
When you die, you descend into Sedna’s realm for purification, punishment or preservation. Once you’ve entered her deathly deep freeze, it can take a very long time to defrost. Any living person foolish enough to visit must negotiate endless spinning circles of ice, and cauldron stews of seal meat bubbling and boiling forever. Inuit Stories of Long Ago - Voices of Inuit - Our Voices, Our Stories: Archived Content This archived Web page remains online for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes.
This page will not be altered or updated. Web pages that are archived on the Internet are not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards. Inuit Games & Recreation – Teacher as Researcher. The life of the Inuit was not all hard work.

As long as there was plenty of food and no immediate chores to be done, or when a severe winter storm kept everyone house-bound, there was time to indulge in pastimes. One pastime the Inuit children enjoyed was games. Children spent a lot of time outside playing tag or hide and seek or pretending to hunt. But there were other games for the young and old during the long, dark winter months, when there was little else to do. Family and Tribal Structure - All about the Inuits: For Kids! Families are really important in Inuit society, because they are the building blocks of the larger society as a whole.
This is how they are grouped for culture, hunting, and supporting one another. To understand the Inuit family and tribal structure, we thought about the following questions: How are they organized within in the family? What are the roles for boys and girls? Cookie Consent and Choices. Native American Legends (D-H). Inuit Gods. Agloolik Good spirit that lived under the ice and helped with hunting and fishing. Aipalovik. Indigenous Peoples Atlas of Canada.
At specific times of the year — when the sun returns to end the long, dark winter night, at the beginning of springtime and when summer finally arrives — communities all across Nunavut stage celebrations and games.
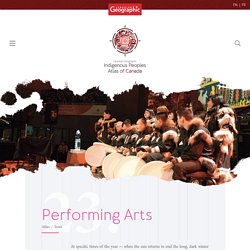
These events include traditional Inuit performing arts such as storytelling, throat singing and drum dancing. During these times, Inuit participate in many traditional Inuit games, which are athletic competitions of strength, agility, dexterity and stamina based on critical skills honed for excellence in hunting and Arctic survival. Inuit Art Information from choosing sculptures and prints, caring for your art, Inuit culture and a look inside an Inuit Artist's studio, including Inuit Art export restrictions. The Inuit are an aboriginal people who are indigenous to the Arctic region of Canada.
For more than 5,000 years the Inuit have lived along the Arctic coast line and on the islands of Canada’s far north. This treeless tundra area, the Canadian Arctic, is often perceived to be one of the most inhospitable regions of the world. Canadian Inuit literature: The development of a tradition on JSTOR. .: INUIT MYTHOLOGY:. The educational attainment of Aboriginal peoples in Canada. Box 1: National Household Survey This is the second release of data from the National Household Survey (NHS).
Roughly 4.5 million households across Canada were selected for the NHS, representing about one-third of all households. This NHS in Brief article complements the analytical document Education in Canada: Attainment, Field of Study and Location of Study, Catalogue no. 99-012-X2011001. Further information on the National Household Survey can be found in the National Household Survey User Guide, Catalogue no. 99-001-X. EconEdLink - Traditional Economies and the Inuit. NPR Cookie Consent and Choices. Demographic variation and change in the Inuit Arctic. Arctic societies, like Arctic environments, display wide variability and often rapid change.
Arctic social and environmental changes are sometimes interconnected, as when industrial development affects ecosystems, or warming climate impacts livelihoods and infrastructure of Arctic residents. Arctic societies also are buffeted by socioeconomic forces, however, which can create problems or drive changes that overlap with or eclipse those from environmental roots. Nunatsiavut Government. The Labrador Inuit Land Claims Agreement set a precedent by including self-government provisions within the land claim.
Nunatsiavut is the first of the Inuit regions in Canada to have achieved self-government. The Nunatsiavut Government is an Inuit regional government. Although Nunatsiavut remains part of Newfoundland and Labrador, the government has authority over many central governance areas including health, education, culture and language, justice, and community matters. Inuktitut: In the Way of the Inuit - the Inuktitut language - Project Naming.
Inuktitut: In the Way of the Inuit Inuktitut is the traditional oral language of Inuit in the Arctic.

Spoken in Canada and Greenland, as well as in Alaska, Inuktitut and its many dialects are used by peoples from region to region, with some variations. For thousands of years, from one generation to the next, Inuit have passed on their stories and legends through the spoken word and in song. Through contact with missionaries from the outside world, a written system was brought to Arctic peoples and developed, as a way of introducing them to Christianity and the Bible. Climate vs. Weather. What is the difference between weather and climate? Weather is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere, and its short-term variation in minutes to weeks.
People generally think of weather as the combination of temperature, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, visibility, and wind. We talk about changes in weather in terms of the near future: "How hot is it right now? " "What will it be like today? " Arctic Weather. Here a German researcher is fixing an instrument called a pyranometer (in the tube). he is trying to collect weather data while on an Arctic ice floe. A pyranometer measures solar radiation. Figure from the NSIDC Arctic Climatology and Meteorology Primer The Arctic or the Earth's Northern Polar Region has pretty extreme weather! Ok, so you know the Arctic is cold, right? Arctic Location and Geography. Home » Arctic: Frozen Ocean Introduction » Geography Arctic: Location and Geography Click here to see different boundaries of the Arctic » The Arctic is named for the north polar constellation “Arktos”—Greek for “bear.” It is 14.5 million square km (5.5 million square miles)—almost exactly the same size as Antarctica—and has been inhabited by humans for close to 20,000 years.
National Geographic Society. The Arctic is the northernmost region of Earth. Most scientists define the Arctic as the area within the Arctic Circle, a line of latitude about 66.5° north of the Equator. Within this circle are the Arctic ocean basin and the northern parts of Scandinavia, Russia, Canada, Greenland, and the U.S. state of Alaska. The Arctic is almost entirely covered by water, much of it frozen. Some frozen features, such as glaciers and icebergs, are frozen freshwater. In fact, the glaciers and icebergs in the Arctic make up about 20% of Earth’s supply of freshwater. Inuit Myth and Legend. Inuit Statistical Profile. The Inuit. Traditional Inuit Beliefs. Arctic - Climate.