

Understanding Evolution. The Age of the Universe. Daniel Perley Table of Contents Introduction One of the simplest, and most scientifically important, questions one can ask is the age of the universe we inhabit.

Under Big Bang cosmology this value, "to", simply refers to the time elapsed since the Big Bang itself, though in fact it could just as well apply (and be measured) had Big Bang model proved incorrect. Age of the Universe. Distance measures (cosmology) Distance measures are used in physical cosmology to give a natural notion of the distance between two objects or events in the universe.
They are often used to tie some observable quantity (such as the luminosity of a distant quasar, the redshift of a distant galaxy, or the angular size of the acoustic peaks in the CMB power spectrum) to another quantity that is not directly observable, but is more convenient for calculations (such as the comoving coordinates of the quasar, galaxy, etc.). The distance measures discussed here all reduce to the common notion of Euclidean distance at low redshift. In accord with our present understanding of cosmology, these measures are calculated within the context of general relativity, where the Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker solution is used to describe the universe. , cosmic or conformal time as well by performing a simple transformation of variables. Cosmological principle. Astronomer William Keel explains: The cosmological principle is usually stated formally as 'Viewed on a sufficiently large scale, the properties of the Universe are the same for all observers.' This amounts to the strongly philosophical statement that the part of the Universe which we can see is a fair sample, and that the same physical laws apply throughout.
In essence, this in a sense says that the Universe is knowable and is playing fair with scientists.[1] The cosmological principle contains three implicit qualifications and two testable consequences. Uniformitarianism. Have physical constants changed with time? [Physics FAQ] - [Copyright] Extra references added 2005.

Original by Steve Carlip. Boston College Front Row - God, Darwin, and Design: America's New Battle Over Evolution. Evolution: How We Know it Happened & Why it Matters (with Dr. Donald Prothero) The Talk.Origins Archive: Evolution FAQs. An Index to Creationist Claims. Creationist claims are numerous and varied, so it is often difficult to track down information on any given claim.
Plus, creationists constantly come up with new claims which need addressing. This site attempts, as much as possible, to make it easy to find rebuttals and references from the scientific community to any and all of the various creationist claims. It is updated frequently; see the What's New page for the latest changes. Since most creationism is folklore, the claims are organized in an outline format following that of Stith Thompson's Motif-Index of Folk-Literature. Sections CA through CG deal with claims against conventional science, and sections CH through CJ contain claims about creationism itself. This collection is intended primarily as a guidepost and introduction. The Complete List Links to Main Sections Expanded Outline.
29+ Evidences for Macroevolution: The Scientific Case for Common Descent. Volution, the overarching concept that unifies the biological sciences, in fact embraces a plurality of theories and hypotheses.

In evolutionary debates one is apt to hear evolution roughly parceled between the terms "microevolution" and "macroevolution". Microevolution, or change beneath the species level, may be thought of as relatively small scale change in the functional and genetic constituencies of populations of organisms. That this occurs and has been observed is generally undisputed by critics of evolution. What is vigorously challenged, however, is macroevolution. The Origin of Life. <address class="plus0">Albrecht Moritz</address><p align=center style='text-align:center'><i>Our apologies, but you must have JavaScript enabled to view author contact information.

</i></p> Copyright © 2010 [Posted October 31, 2006] Update July 1, 2010 Abstract Even the simplest currently living cells contain hundreds of proteins most of which are essential to their functioning. Contents 1. Cience shows us that the universe evolved by self-organization of matter towards more and more complex structures. Upon considering this self-organization of material structures in the realm of philosophy, one may conclude that it happens either because the underlying laws of nature, which have to be exceedingly special to allow for it (Rees 2001, Smolin 1999, Susskind 2006), simply are the way they are (possibly in the context of a multiverse) or because they were designed by God for this purpose. 2.
How do species evolve different numbers of chromosomes? Re: How do species evolve different numbers of chromosomes?

Area: Genetics Posted By: John Franklin Rawls, grad student, Developmental Biology, Washington University Date: Sun Sep 28 19:28:43 1997 Area of science: Genetics ID: 875201002.Ge Message: Hello there! Chimp genome : Web focus : Nature. In this focus: Current research | Archive What makes us human?
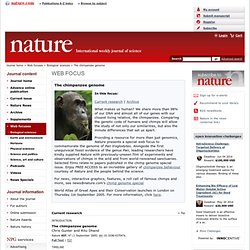
We share more than 98% of our DNA and almost all of our genes with our closest living relative, the chimpanzee.