

The American Journal of International Law, Vol. 78, No. 2 (Apr., 1984), pp. 427-440. Black Book Of The Admiralty Vol. 1 1871. The Treaty of Westphalia. The Economic Policy That Made the Peace of Westphalia by Pierre Beaudry May, 2003 (EIR) In view of the currently collapsing world financial system, which is tearing apart the Maastricht Treaty, European governments have a last opportunity to abandon the failed Anglo-Dutch liberal system of private central banking and globalization, and organize the new Eurasian axis of peace centered on Russia, Germany, and France.
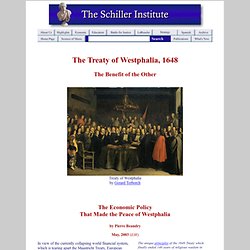
Treaty of Westphalia, 1648. International History.

OSTF Declaration of Sovereignty and Nationhood - Original Sovereign Tribal Federation. NY LawFund: Know Your Escrow Rights. About this pamphlet Consumers in New York State are frequently required to participate in escrow transactions.

This pamphlet has been prepared by the New York Lawyers' Fund for Client Protection as a plain-English guide to the rights of consumers and law clients, and the fiduciary obligations of escrow agents. The practical suggestions in this pamphlet are based upon New York laws, rules and court decisions. Observing them will help consumers avoid disagreements in escrow transactions, and prevent the misuse or loss of escrow money and property. Because escrow agreements are legal contracts that involve important rights and obligations, the careful consumer will consult a lawyer before entrusting money or property with an escrow agent. What's an escrow? An escrow is a legal arrangement to help parties perform their contracts and avoid disagreements. Globalization and Autonomy. Welcome to the Globalization and Autonomy Online Compendium, a collective publication by the team of leading Canadian and international scholars who are part of the SSHRCC Major Collaborative Research Initiative on Globalization and Autonomy.
Using the Compendium, the team is making the results of their research available to a wide public audience. Team members have prepared a glossary of hundreds of short articles on relevant persons, places, organizations, events and key concepts and compiled an extensive searchable bibliographical database. They have written short summaries of their research that will be published in academic form in the 10-volume UBC Press "Globalization and Autonomy Series: Dialectical Relationships Shaping the Contemporary World.
" Finally, the Compendium contains position papers and peer-reviewed research articles on globalization and autonomy issues. INTERNATIONAL PARLIAMENT » Presentazione Parlamento. Manila Declaration on the Peaceful Settlement of International Disputes - Main Page. Introduction The Manila Declaration on the Peaceful Settlement of International Disputes (hereinafter Manila Declaration or Declaration) was approved by resolution 37/10 (under the item Peaceful settlement of disputes between States) 1 by the United Nations General Assembly on 15 November 1982, on the basis of a text prepared by the Special Committee on the Charter of the United Nations and on the Strengthening of the Role of the Organization at its 1980 session, held in Manila, the Philippines.
The Declaration is the first important instrument of the work of the Special Committee on the Charter of the United Nations and on the Strengthening of the Role of the Organization, and one of its significant achievements. 2 The Manila Declaration was elaborated on the initiative of non-aligned countries (Egypt, Indonesia, Mexico, Nigeria, Philippines, Romania, Sierra Leone, and Tunisia). 3 The Declaration contains a preamble and two operative parts. Preamble Part. Related Materials A. B. C. D. C. Resource Guide to the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
The definitive guide to complying with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, written by those in charge of enforcing it: The Securities and Exchange Commission and the Department of Justice.
From the SEC website: "The guide provides helpful information to enterprises of all sizes from small businesses doing their first transactions abroad to multi-national corporations with subsidiaries around the world. The Peaceful Settlement of International Disputes. Abstract.
Democratic Disobedience: Reconceiving Self-Determination and Secession(.pdf) Global Reach and Limitations of Self-Determination (.pdf) Max Planck Encyclopedia of Public International Law - sample article. Globalization and Autonomy. Julie Sunday, McMaster University In general terms, self-determination is the right of a national group to be sovereign within a given territory. Although this definition appears to be straightforward, applying it consistently has proved extremely difficult. Are only nation-states allowed to be self-determining or are national minorities within states also entitled to self-determination? Self-determination can therefore be interpreted in two distinct and conflicting ways. On the one hand, all national groups should be entitled to self-determination. Self-Determination Procedures. Since the end of the Cold War, more and more groups of people have demanded the right to "self-determination", meaning they have demanded their own nation-state or some degree of autonomy within another nation state.
The demands may be political — groups may want sovereignty or a greater political "voice" in the governmental structure, or they may be cultural — wanting the right to preserve their own language, cultural traditions, and "way of life. " (Or they may be both.) The responses to these demands have been quite varied, ranging from complete denial (through ignoring the demands, or repressing them) to trying to accommodate them to lesser or greater degrees. Often considerable conflict emerges before an accommodation (of whatever kind) is worked out. In order for these conflicts to be resolved, steps must be taken to address the desire for self-determination. World Civil Society Forum Official Report. Coordinator Joshua Cooper (Hawaii Institute for Human Rights) Co-coordinator Nicolas Guerrero (Mandat International) Assistance Mélanie Clerc (Mandat International)

HagueAgendaPeace+Justice4The21stCentury.pdf (application/pdf Object) International Organizations N - W. About UNPO. INDEXTitle I: General ProvisionsTitle II: Provisions Governing ParticipationTitle III: Provisions Governing InstitutionsSection I: The Assembly Section II: The PresidencySection III: The Secretariat Section IV: Regional Chapters Title IV: Financial ProvisionsTitle V: Suspension and Termination of ParticipationTitle VI: Liquidation of the OrganizationTitle VII: Amendments to the Covenant Affirming the principles of Democracy, as enshrined in the Vienna declaration, as fundamental and inalienable human rights; Noting that political and civil rights are guaranteed to individuals and communities through international law and binding covenants, such as the International Covenants on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights; Aware that individual rights are inextricably linked to the recognition and protection of collective rights, as well as the free expression of collective identity, religious beliefs, and dignity; Title I Title II.

Legal Definition of Immunity. Immunity Exemption from performing duties that the law generally requires other citizens to perform, or from a penalty or burden that the law generally places upon other citizens.
Sovereign Immunity Sovereign Immunity prevents a sovereign state or person from being subjected to suit without its consent. Immunities of State Officials, International Crimes, and Foreign Domestic Courts. ↵ 1 See, generally, Whomersley, ‘Some Reflections on the Immunity of Individuals for Official Acts’, 41 (1992) 848; Tomonori, ‘The Individual as Beneficiary of State Immunity: Problems of the Attribution of Ultra Vires Conduct’, 29 (2001) 261; H.

Fox, (2nd edn, 2008), at 455–464 and Ch. 19; Watts, ‘The Legal Position in International Law of Heads of States, Heads of Governments and Foreign Ministers’, 247 (1994-III) 13; Wickremasinghe, ‘Immunities Enjoyed by Officials of States and International Organizations’, in M. Evans (ed.), (3rd edn, 2010), at 380. ↵ 2 Akande, ‘International Law Immunities and the International Criminal Court’, 98 (2004) 407, 409–415. ↵ 3 See Watts, note 1. ↵ 4 E.g., Arts 29 and 31 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations 1961 (VCDR), 500 UNTS 95; Art. . ↵ 5 Arts 21, 39, and 31 UN Convention on Special Missions 1969, 1400 UNTS 231. Sovereign Immunity. In constitutional monarchies the sovereign is the historical origin of the authority which creates the courts. Thus the courts had no power to compel the sovereign to be bound by the courts, as they were created by the sovereign for the protection of his or her subjects.
By country[edit] Australia[edit] There is no automatic Crown immunity in Australia, although the Crown may be explicitly or implicitly immune from any particular statute. There is a rebuttable presumption that the Crown is not bound by a statute: Bropho v State of Western Australia.[1] The Crown's immunity may also apply to other parties in certain circumstances: see Australian Competition and Consumer Commission v Baxter Healthcare.
Belgium[edit] Standards on Prosecutorial Investigations (Table of Contents) GUIDE TO CRIMINAL PROSECUTIONS IN THE UNITED STATES. In addition to the “Guide to Criminal Prosecutions in the United States” set forth below, and provide general information about the United States and its legal system, including the courts. "The Continuing question of sovereignty and the Sovereign Military Order of Jerusalem, of Rhodes and of" [2006] ALRS 10; (2006) 13 Australian International Law Journal 211-232. You are here: AustLII >> Databases >> ALTA Law Research Series >> 2006 >> [2006] ALRS 10 Database Search | Name Search | Recent Articles | Noteup | LawCite | Author Info | Download | Help Last Updated: 16 August 2010.
Primer on International Law « The Burney Law Firm, LLC. Self Determination: Principle & the Law - சுயநிர்ணய உரிமை Fourth World - Nations without a State. Nadesan Satyendra May 2000, March 2007 "Increasingly, the Fourth World is emerging as a new force in international politics because in the common defense of their nations, many indigenous peoples do not accept being mere subjects of international law and state sovereignty and trusteeship bureaucracies.
Instead, they are organizing and exerting their own participation and policies as sovereign peoples and nations. " - Bernard Q. Refugess and Stateless Persons. Self-determination and secession under international law. - Denver Journal of International Law and Policy - Nbr. 2001 - Author: Nanda, Ved P. - Id 56468866 - vLex. Beyond Territory: Revisiting the Normative Justification of Self-Government in Theory and Practice. Beyond Territory: Revisiting the NormativeJustification of Self-Government in Theory andPractice. Self Determination: Sovereignty, Territorial Integrity, and the Right to Secesssion. Self-determination: origins and meaning by David Fromkin for The Wall Street Journal. Written by David Fromkin for The Wall Street Journal (31 March 1999) Internation Human Rights Law and the Role of the Legal Professions: A general Intro. The Hague Academy of International Law - Home. Brill: Martinus Nijhoff Online. Nijhoff Online. Peace Palace Library, the international law library.
International Dispute Settlement. Organization of American States - Official Documents. Each year the OAS Secretary General publishes a proposed Program-Budget for the coming calendar year. American Declaration of the Rights and Duties of Man. American Convention on Human Rights. [Signatories and Ratifications] Lenin: The Right of Nations to Self-Determination.
The Right of Nations to Self-Determination. INTERPOL. UNPO: Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. General introduction to the standard-setting instruments of UNESCO. Standard-Setting Instruments. Conventions.
What is Self Determination? (UNPO) Self determination and conflict transformation. THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RIGHT TO SELF DETERMINATION.