

I believe that most of you here may and can understand what it's like to be a teenager all over again. Now, were you often misunderstood for the things you have done which you thought was good? And were you often scolded and reprimanded by your parents? How so? And do you remember how you felt? Good, bad? Happy, sad?
Fast forward to many years later, and its now your turn to parent your teenager who may display some desirable or undesirable behaviours . Let's look into reinforcements and punishments and how these can help influence your teenage children's behaviours.
Positive and Negative reinforcements and behaviours. Learning: Negative Reinforcement vs. Punishment. Reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement. Negative Reinforcement. Positive vs. Negative Reinforcement. The Difference Between Positive and Negative Reinforcement - Danielle Forshee, Psy.D, LCSW. Behavioral issues can begin at a young age and carry on through a person’s entire life if not dealt with accordingly.

Reinforcement is what we use to help increase the probability that a behavior will occur with the use of a stimulus or item as soon as the required response or behavior is shown. If this doesn’t make sense, in simple terms; it is a reward for a certain behavior. Punishment. Postive Punishment. Negative Punishment. Positive vs. Negative Punishment. Teenagers. Erik Erikson's Psychosocial Theory. Erik Erikson's Psychosocial theory: Identity vs Role confusion. Desirable Teenage Behaviours. Undesired Teenage behaviours. The use of positive and negative reinforcements. BYU Study: a need for positive reinforcement among teens. There are countless publications describing the best ways to raise a child in the hopes of them becoming successful adults.
Between the books, magazines and video tutorials, parents may be finding themselves overwhelmed on more than one occasion. But a group of researchers at Brigham Young University have found the answer to helping children through life may be less complicated than it seems. The BYU study found bad behavior can be discouraged among children by simply encouraging good behavior. The study, Flourishing During the Teen Years: Why “Not Being Bad” Isn’t Good Enough, used information from a 10-year project that followed 500 families in order to see where the individuals struggled and what actions helped them become successful.
When the study began, the children in the families were 11 years old. How to Reward Your Teen for Good Behavior. Teenagers are young adults who are trying to learn the ways of the world.

When they do something great at school or at home or simply make a healthy decision, parents can give them a reward. The reward does not have to be money, but it is a nice way to say "thank you" or "I'm proud of you. " Teens need this positive reinforcement because it shows them that they are on the right track.1 It is also a good life lesson that you can pass on: good things happen to good people. The use of positive and negative punishments for parents. What is Negative Punishment (Examples and Effectiveness) In this article, we will review negative punishment, its definition, examples, and drawbacks.

American psychologist B.F. Skinner developed the theory of operant conditioning, which stated that a person or animal’s behavior could be increased or decreased by adding or removing appropriate stimuli after the behavior is exhibited. The difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning is that classical affects unconscious behavior, while operant affects conscious behavior.
Within operant, punishment aims to reduce a behavior while reinforcement increase a behavior. Waldentwo: Positive and Negative reinforcement. Negative reinforcement is a term described by B.F.
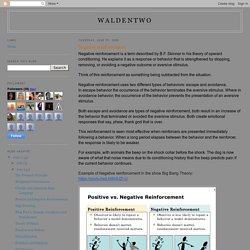
Skinner in his theory of operant conditioning. He explains it as a response or behavior that is strengthened by stopping, removing, or avoiding a negative outcome or aversive stimulus. Think of this reinforcement as something being subtracted from the situation. Positive vs Negative Punishment - Psychestudy. Punishment is a fundamental concept of Operant Conditioning, whose major objective is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior from occurring again.
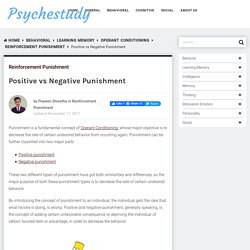
Punishment can be further classified into two major parts These two different types of punishment have got both similarities and differences, as the major purpose of both these punishment types is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior. By introducing the concept of punishment to an individual, the individual gets the idea that what he/she is doing, is wrong.
Positive and negative punishment, generally speaking, is the concept of adding certain unfavorable consequence or depriving the individual of certain favored item or advantage, in order to decrease the behavior. Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development & High School Students. Erik Erikson (1902-1994) was a pupil of Sigmund Freud and the first child psychoanalyst in Boston.

After extensive study of children from various cultural backgrounds and areas he began to compile this information to form his theories on development, personality, and what forms our identity. Erikson’s theory breaks down psychosocial development into eight (and eventually a final ninth) stages. Operant Conditioning - Parenting 101. Discipline for Teens: Strategies and Challenges. When your child becomes a teenager, your parenting role is likely to shift.

You may find yourself becoming more of a guide, rather than an enforcer. That’s not to say your child won’t need you to intervene when there are safety issues or that your teen won’t need consequences. But, by now, it’s OK to let your child make some choices on their own, even when you think it’s a bad choice. Typical Teen Behavior. References. References.