

Mur. Add Letters » Custom Picture of Fridge Letters! A ransom note generator. Save the drama for your mama sign. Question-able Material. Many students on my caseload have language difficulties impacting their ability to answer simple questions — a deficit that has the potential for considerable effects on a student’s ability to perform successfully in their educational environment.
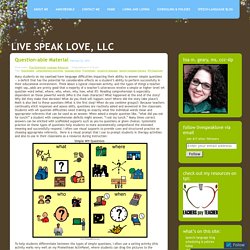
Think about a typical classroom activity, and the types of things a teacher might say…odds are pretty good that a majority of a teacher’s utterances involve a simple or higher level wh question word (what, where, who, when, why, how, what if?) Reading comprehension is especially dependent on these powerful words (Who is the main character? What happened at the end of the story? Why did they make that decision? What do you think will happen next? Free Teacher Resources. Classroom Posters For Every Teacher (Light Bulbs and Laughter) [activité libre] les blasons autonomie cycle 3.
The pronunciation of S at the end of plural nouns, verbs in third person and as a part of the possessive case sometimes causes problems for non-native speakers because it can be pronounced in three different ways: / ɪz /, / s / or / z /.
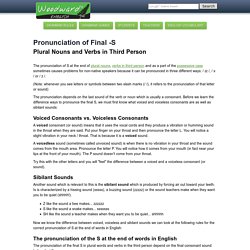
(Note: whenever you see letters or symbols between two slash marks (/ /), it refers to the pronunciation of that letter or sound) The pronunciation depends on the last sound of the verb or noun which is usually a consonant. Before we learn the difference ways to pronounce the final S, we must first know what voiced and voiceless consonants are as well as sibilant sounds: Voiced Consonants vs. ED appears at the end of regular verbs in the past tense (e.g. wanted, helped, lived) sometimes in adjectives ending in ED (e.g. tired, embarrassed, relaxed) as well as in some Past Participles.

However the pronunciation of ED sometimes causes problems for non-native speakers because it can be pronounced in three different ways: as / id /, as / t / or as / d / (Note: whenever you see letters or symbols between two slash marks (/ /), it refers to the pronunciation of that letter or sound) Before we learn the difference ways to pronounce ED, we must first know what voiced and voiceless consonants are. Voiced Consonants vs. What is the difference between United Kingdom, Great Britain and the British Isles?
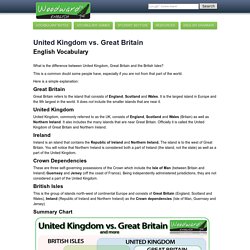
This is a common doubt some people have, especially if you are not from that part of the world. Here is a simple explanation: Great Britain Great Britain refers to the island that consists of England, Scotland and Wales. It is the largest island in Europe and the 9th largest in the world. United Kingdom United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the UK, consists of England, Scotland and Wales (Britain) as well as Northern Ireland. Ireland Ireland is an island that contains the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. Crown Dependencies These are three self-governing possessions of the Crown which include the Isle of Man (between Britain and Ireland) Guernsey and Jersey (off the coast of France).
British Isles Summary Chart If you found this English Vocabulary about United Kingdom vs. Vocabulary Notes. English Teachers: If you would like to use this Question Words wall chart in your classroom, then you can purchase a copy here: Question Words Wall Chart and Flash Cards.

The most common question words in English are the following: WHO is only used when referring to people. (= I want to know the person) We use some adverbs to describe how frequently we do an activity.
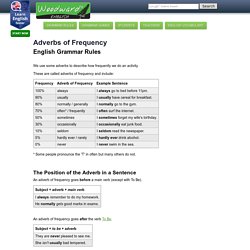
These are called adverbs of frequency and include: * Some people pronounce the 'T' in often but many others do not. The Position of the Adverb in a Sentence An adverb of frequency goes before a main verb (except with To Be). An adverb of frequency goes after the verb To Be. When we use an auxiliary verb (have, will, must, might, could, would, can, etc.), the adverb is placed between the auxiliary and the main verb. We can also use the following adverbs at the start of a sentence: Usually, normally, often, frequently, sometimes, occasionally Occasionally, I like to eat Thai food. BUT we cannot use the following at the beginning of a sentence: Always, seldom, rarely, hardly, ever, never.
We use hardly ever and never with positive, not negative verbs: She hardly ever comes to my parties. We use ever in questions and negative statements: Have you ever been to New Zealand? Next activities. Despite a weird name, reflexive pronouns are helpful tools in English grammar, and they are easy to use.
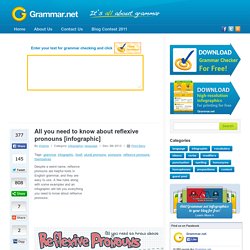
A few rules along with some examples and an infographic will tell you everything you need to know about reflexive pronouns. <a href=" src= alt="Grammar.net" /></a> [Infographic provided by <a href=" To download high resolution poster click here. A Pronoun Refresher. If you would like to learn about conditionals and when to use whether or if, this infographic can help.
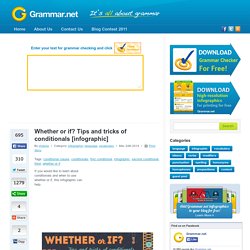
<a href=" src= alt="Grammar.net" /></a> [Infographic provided by <a href=" To download high resolution poster click here. What is a Conditional? A grammar device that shows possible results from certain situations is called a “conditional.”