

E-learning for kids. Home. The eLearning Guild: Community & Resources for eLearning Professionals. Educational technology. Use of technology in education to improve learning and teaching Educational technology (commonly abbreviated as EduTech, or EdTech) is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning.[1] When referred to with its abbreviation, EdTech, it is often referring to the industry of companies that create educational technology.[2][3] Definition[edit] Accordingly, there are several discrete aspects to describing the intellectual and technical development of educational technology:
Home. MERLOT II - Home. ADDIE. Office: S 316M Phone:415 452-5699 Email mmalacho@ccsf.edu Dr.

Malachowski's Home Page Table of Contents Abstract Instructional Design Events of Instruction ARCS Model Constructivism References Abstract. The ADDIE Process - Intulogy.com. The ADDIE instructional design model forms a roadmap for the entire training project.

Intulogy uses this popular instructional design model to help our clients analyze their training needs, design and develop training materials, implement training, and evaluate its effectiveness. Sometimes, Intulogy works directly with a client’s training specialists, who have studied the ADDIE model in graduate school. However, we’re often contacted by directors and executives who know their company has a training need, but they don’t know much about the instructional design process. Intulogy’s training specialists share a flowchart of the ADDIE instructional design model with our clients. It helps our clients locate where they are in the training project lifecycle, and it provides a common language for us to discuss the project.
Going through the ADDIE steps can answer many common questions about a training project: Why should you use the ADDIE methodology for your company’s training? Soon after the U.S. Understanding by Design Framework. Resources « McTighe & Associates. Understanding by Design. Understanding by Design, or UbD, is a tool utilized for educational planning focused on "teaching for understanding" advocated by Jay McTighe and Grant Wiggins in their Understanding by Design (1998), published by the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.[1][2] The emphasis of UbD is on "backward design", the practice of looking at the outcomes in order to design curriculum units, performance assessments, and classroom instruction.[3] "Understanding by Design" and "UbD" are registered trademarks of the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development ("ASCD").
According to Wiggins, "The potential of UbD for curricular improvement has struck a chord in American education. Over 250,000 educators own the book. Over 30,000 Handbooks are in use. More than 150 University education classes use the book as a text. Instructional design. Process for design and development of learning resources Instructional design (ID), also known as instructional systems design (ISD), is the practice of systematically designing, developing and delivering instructional products and experiences, both digital and physical, in a consistent and reliable fashion toward an efficient, effective, appealing, engaging and inspiring acquisition of knowledge.[1][2] The process consists broadly of determining the state and needs of the learner, defining the end goal of instruction, and creating some "intervention" to assist in the transition.
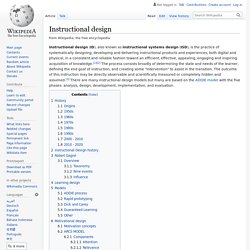
The outcome of this instruction may be directly observable and scientifically measured or completely hidden and assumed.[3] There are many instructional design models but many are based on the ADDIE model with the five phases: analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation. History[edit] Origins[edit] 1950s[edit] B. 1960s[edit] Robert Glaser introduced “criterion-referenced measures” in 1962. Instructional Design. InstructionalDesign. Intro eLearn. Course Module Evaluation Rubric. A Rubric for Evaluation Online Course Modules This rubric, or instrument, should be used by course developers to develop quality online course modules.
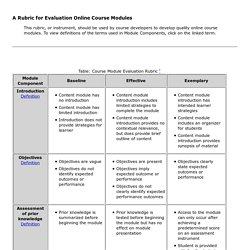
To view definitions of the terms used in Module Components, click on the linked term. Definition of terms Introduction By providing an introduction, you are offering your perspective on the content for the students. To top of page Objectives By providing objectives, students will know not only what they are expected to do as a result of the learning, but also how they will be evaluated in the learning process.
Assessment of prior knowledge Many times this has been referred to as a pre-test. Readings This may often be referred to as supplemental material or readings. Content pages Content is the heart of the content module. Assignments Assignments are those elements that are products, outcomes, or measurable events. Assessment Assessment is the true measure as some would say as to whether or not learning has occurred. Group work. Five tips for designing effective online learning modules. Online learning makes it easy for students to learn what they need to move ahead in their training, courses, or careers.
Whether you're designing your original content in Word, PowerPoint, or Excel, when you add it to a Learning Content Management System (LCMS), the way you organize your content can help students learn the material successfully. The learning modules you design will be effective for students if you create a logical structure, reinforce key concepts, and add exercises at just the right points to help students evaluate their own learning. 1: Outline your session Perhaps the most important element in an effective online learning module is the way in which it is organized.
Your students need to know what the major tasks in the lesson will be. 2: Create sections for major steps in the process Design your learning module so that each major task is its own section. 3: Make your introductions clear.