

An Eye in the Sky for Boots on the Ground. Information technology in India. Information technology in India is an industry consisting of two major components: IT Services and business process outsourcing (BPO).
The sector has increased its contribution to India's GDP from 1.2% in 1998 to 7.5% in 2012.[1] According to NASSCOM, the sector aggregated revenues of US$100 billion in 2012, where export and domestic revenue stood at US$69.1 billion and US$31.7 billion respectively, growing by over 9%.[1] The major cities that account for about nearly 90% of the sector's exports are Bangalore, Chennai, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Trivandrum, Noida, Mumbai and Pune. Bangalore is considered to be the Silicon Valley of India because it is the leading IT exporter.[3][4] Exports dominate the industry and constitute about 77% of the total industry revenue.
However, the domestic market is also significant with a robust revenue growth.[1] The industry’s share of total Indian exports (merchandise plus services) increased from less than 4% in FY1998 to about 25% in FY2012. What is IT? - IT impact on Daily life. IT People. Steve Jobs. Steve Jobs, CEO. Bill Gates, Microsoft. Steve Shirley. Richard Stallman. American free software activist Richard Matthew Stallman (; born March 16, 1953), often known by his initials, rms,[1] and occasionally upper-case RMS, is an American free software movement activist and programmer.
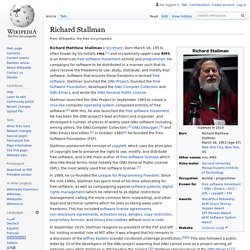
He campaigns for software to be distributed in a manner such that its users receive the freedoms to use, study, distribute, and modify that software. Software that ensures these freedoms is termed free software. Stallman launched the GNU Project, founded the Free Software Foundation, developed the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Emacs, and wrote the GNU General Public License. Stallman launched the GNU Project in September 1983 to create a Unix-like computer operating system composed entirely of free software.[2] With this, he also launched the free software movement. File:Tim Berners-Lee-Knight-crop.jpg. Clarke's three laws. Clarke's Three Laws are three "laws" of prediction formulated by the British science fiction writer Arthur C.
Clarke. They are: When a distinguished but elderly scientist states that something is possible, he is almost certainly right. When he states that something is impossible, he is very probably wrong.The only way of discovering the limits of the possible is to venture a little way past them into the impossible.Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic. Origins[edit] Clarke's First Law was proposed by Arthur C. The second law is offered as a simple observation in the same essay. Gates, S. James Jr. - University System of Maryland Regents Professor, John S. Toll Professor of Physics, and Center for String & Particle Theory Director.
Linus Torvalds. Linus Benedict Torvalds (Swedish: [ˈliːn.ɵs ˈtuːr.valds] ( Biography[edit] Early years[edit] Torvalds was born in Helsinki, Finland.
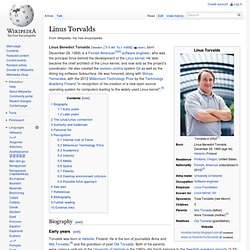
He is the son of journalists Anna and Nils Torvalds,[6] and the grandson of poet Ole Torvalds. Both of his parents were campus radicals at the University of Helsinki in the 1960s. Torvalds attended the University of Helsinki between 1988 and 1996, graduating with a master's degree in computer science from NODES research group.[8] His academic career was interrupted after his first year of study when he joined the Finnish Army, selecting the 11-month officer training program to fulfill the mandatory military service of Finland. His interest in computers began with a Commodore VIC-20.[12] After the VIC-20 he purchased a Sinclair QL, which he modified extensively, especially its operating system. Later years[edit] From 1997 to 1999 he was involved in 86open helping to choose the standard binary format for Linux and Unix.
The Linus/Linux connection[edit] Martha Lane Fox, Baroness Lane-Fox of Soho. Martha Lane Fox, Baroness Lane-Fox of Soho,[1] CBE (born 10 February 1973) is an English businesswoman, philanthropist, and public servant.
She co-founded Lastminute.com in the dotcom boom of the early 2000s and has subsequently served on public service digital projects. She is a board member of Channel 4, mydeco.com, Marks & Spencer, and chairs the board of the digital skills charity, Go ON UK. Lane Fox joined the House of Lords as a crossbencher on 26 March 2013, becoming its youngest female member.[2] Lane Fox was also appointed as Chancellor of the Open University as of 12 March 2014.[3] Edgar F. Codd. Edgar Frank "Ted" Codd (19 August 1923 – 18 April 2003) was an English computer scientist who, while working for IBM, invented the relational model for database management, the theoretical basis for relational databases.
He made other valuable contributions to computer science, but the relational model, a very influential general theory of data management, remains his most mentioned achievement.[6][7] Biography[edit] Edgar Frank Codd was born on the Isle of Portland in England. After attending Poole Grammar School, he studied mathematics and chemistry at Exeter College, Oxford, before serving as a pilot in the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. In 1948, he moved to New York to work for IBM as a mathematical programmer. WHERE ARE THE FAMOUS IT INDUSTRIES. Poplet IT. IT Industry News. IT Industry India. IT Industry Information and IT Industry Trends. Overview The IT & ITes sector includes IT services, engineering design and R&D services, ITES (IT-enabled services) or BPO and hardware.
Today IT and ITeS sectors lead the economic growth in terms of employment, export promotion, revenue generation and standards of living. As per NASSCOM estimates, IT/ITeS sector (excluding hardware) revenues are estimated at USD 87.6 billion in FY 2011-12; and the industry is expected to grow by 19 per cent during FY 2012-13. The IT/ITeS sector has led to employment opportunities, both direct and indirect, of nearly 2.8 million and around 8.9 million respectively. This growth is expected to increase to more than 14 million (direct and indirect) by 2015 and to around 30 million by 2030. The market size of the industry is expected to rise to USD 225 billion by 2020 considering India's competitive position, growing demand for exports, Government policy support, and increasing global footprint.
Introduction to the terms: Low operating costs and tax advantage.