

Researchers map the impact of human sewage on coastlines around the world. Researchers have mapped the discharge of global wastewater — treated, septic, and raw sewage — into coastal ecosystems in what they say is the finest detail yet.
And the numbers are intimidating. Key points: Researchers found just 25 watersheds contribute half of the total wastewater nitrogen to the world's oceansMeat-heavy diets are a significant factor in nitrogen levels High nitrogen levels can lead to algal blooms. Travis Scott's Astroworld disaster was caused by a 'crowd surge', a deadly risk that lurks at all mass gatherings. In every crowd crush, there's a terrifying moment when the mood goes from a little messy to deadly.
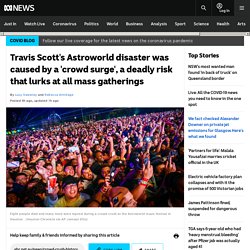
Gaby Simeoni realised she was in grave danger at the Astroworld festival in Houston when rapper Travis Scott was three songs into his set. "Things were getting super hectic, people were falling down, people were passing out, I was stepping on people, you could not move," she said on TikTok. As the 50,000-strong crowd surged towards the stage, Gaby, who is just 147 centimetres tall, felt herself sucked into a pile of heaving bodies. Overview of Environmental Health. Environmental health involves those aspects of public health concerned with the factors, circumstances, and conditions in the environment or surroundings of humans that can exert an influence on health and well-being.
Environmental health provides the basis of public health. Improvements in sanitation, drinking water quality, food safety, disease control, and housing conditions have been central to the significant improvement in quality of life and longevity experienced over the last hundred years. Environmental health practice addresses emerging health risks arising from the pressures that human development places on the environment. Office of Health Protection (OHP) Responsibility for providing advice on environmental health matters to the Minister for Health and a wide range of Commonwealth, State and Territory agencies, industry and the general community rests with the Department's Office of Health Protection. Keeping community safe with public health advice. As part of this, EPA has started work on developing an environmental health tracking network that will allow EPA to identify public health risks and assess their extent, seriousness and trends relating to environmental conditions.
The network will lead to more information-driven decisions and communication, ultimately improving the health of Victorians by reducing the environmental health impacts of pollution and waste. EPA has also established an Environmental Public Health team to provide specialist advice to EPA officers, the community and Victoria’s Chief Environmental Scientist about the public health impacts from past, present and future waste and pollution. For Educators. Health and environment Archives - Right Now. To read In the Eye of the Storm: Volunteers and Australia’s Response to the HIV/AIDS Crisis during another global health crisis is a strange experience.
One is made aware of the disparities in the Australian government’s response to the two events. Between 1956 and 1963, the Australian government authorised British nuclear tests on Anangu country. ‘Old story, new story’ chronicles these events at Maralinga. Air pollution. WHO Expert Consultation: Risk communication and intervention to reduce exposure and to minimize the health effects of air pollution The two-day consultation took place on12–14 February 2019 at WHO headquarters in Geneva.
It included presentations on the current review of evidence, methods and applications, and will include significant time for discussion, identification of data gaps, research needs, and the next steps to derive expert suggestions in a consistent and harmonized approach, while providing elements of guidance in the form of specific and practical advice. View the Expert Consultation homepage for more information Air pollution and health Air pollution kills an estimated 7 million people worldwide every year.
A global map of wind, weather, and ocean conditions. Environment Protection Authority Victoria. Australia State of the Environment Report. National air quality standards The NEPC established national ambient air quality standards in 1998 as part of the National Environment Protection Measure for Ambient Air Quality (Air NEPM).
The Air NEPM sets standards for the 7 key air pollutants to which most Australians are exposed: carbon monoxide, lead, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) and sulfur dioxide (Table ATM4). Integrated Transport and Health Impact Modelling Tool (ITHIM) - MRC Epidemiology Unit. Integrated Transport and Health Impact Modelling Tool (ITHIM) ITHIM refers to a range of related models and tools developed at CEDAR to perform integrated assessment of the health effects of transport scenarios and policies at the urban and national level.

The health effects of transport policies are modelled through the changes in physical activity, road traffic injury risk, and exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution. Some versions of ITHIM also predict changes in CO2 emissions. ITHIM is being used in research and by health and transport professionals to estimate the health impacts of scenarios, compare the impact of travel patterns in different places, and model the impact of interventions. Air quality - AirQ+: software tool for health risk assessment of air pollution. WHO/Europe is interested in gathering information about where and how AirQ+ is used, to improve its assistance.

Please share information on your use of AirQ+. We will use the survey data in aggregated form for a general overview and statistical analysis of AirQ+ users. Quantifying the effects of exposure to air pollution in terms of public health has become a critical component in policy discussion. WHO/Europe's software tool AirQ+ performs calculations that allow quantification of the health effects of exposure to air pollution, including estimates of the reduction in life expectancy. AirQ+ estimates: Transport and health - Health economic assessment tool (HEAT) for cycling and walking. To facilitate evidence-based decision-making, WHO has developed, in collaboration with experts, an online tool to estimate the value of reduced mortality that results from regular walking or cycling.

The health and economic assessment tool (HEAT) for cycling and walking: is intended to be part of comprehensive cost–benefit analyses of transport interventions or infrastructure projects; complements existing tools for economic valuations of transport interventions, for example on emissions or congestion; can also be used to assess the current situation or past investment; is based on best available evidence, with parameters that can be adapted to fit specific situations. Default parameters are valid for the European context. HEAT calculates the answer to the following question: if x people cycle or walk y distance on most days, what is the economic value of mortality rate improvements?
Applications. Urban health - GreenUr: the Green Urban spaces and health tool. The quantification of the impacts of green spaces on health has been attracting increasing attention in political discussions and research activities. The results of several research projects are now converging towards a quantifiable association of the effects of green spaces on health in various populations and on a variety of spatial and temporal scales. Current knowledge on green space measurements and effects adds a public health perspective that is relevant for monitoring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals (in particular Goal 11.7). Urban health - iSThAT: the Integrated Sustainable Transport and Health Assessment Tool.
iSThAT is a simplified methodological framework and accompanying software tool for the evaluation of the health and economic benefits of carbon reduction measures in the context of urban transportation. The tool supports the identification of alternative transportation choices based on sound, reproducible, science-based reasoning. Additionally, it is a user-friendly, interactive Excel-based tool for evaluating carbon mitigation alternatives in surface transportation for informational and educational purposes. iSThAT provides time series results extending from 2015 (base year) to 2050 in year increments, with the output charts showing trends at 1-year resolution. Ambient air pollution: A global assessment of exposure and burden of disease. Ambient air pollution. NSW fires: Air pollution affecting residents' health with increase in PM2.5. Tiny air pollution particles - like the very ones in bushfire smoke swathing NSW - are doing more than aggravating the lungs of asthmatics.
Even short term exposure to the particulate PM2.5 is sending people to hospital for a multitude of newly identified reasons including sepsis and urinary tract infections. Every 0.001 part-per-million of PM2.5 in the air is linked to 2050 extra hospital admissions, 12,216 days in hospital and almost $46 million in healthcare costs for conditions including lung diseases, diabetes, Parkinson's disease and diabetes, a US study published on Thursday in the BMJ found. PM2.5 was also linked to rises in hospitalisations for illnesses not previously associated with the particulate, such as septicaemia, kidney failure, UTIs and skin and subcutaneous tissue infections. Ambient and household air pollution and health. Guidelines. Joint statement: the air pollution in NSW is a public health emergency. 25 health and medical groups have today released a joint statement calling on the Federal and NSW governments to respond to the public health emergency in NSW created by the ongoing air pollution from bushfire smoke.
Smoke from bushfires has produced air pollution of up to 11 times the base ‘hazardous’ level in parts of Sydney and New South Wales. High levels of air pollution are expected to continue. There is no safe level of air pollution. Exposure to outdoor air pollution and its human health outcomes: A scoping review. Abstract Despite considerable air pollution prevention and control measures that have been put into practice in recent years, outdoor air pollution remains one of the most important risk factors for health outcomes.
To identify the potential research gaps, we conducted a scoping review focused on health outcomes affected by outdoor air pollution across the broad research area. Of the 5759 potentially relevant studies, 799 were included in the final analysis. The included studies showed an increasing publication trend from 1992 to 2008, and most of the studies were conducted in Asia, Europe, and North America. Among the eight categorized health outcomes, asthma (category: respiratory diseases) and mortality (category: health records) were the most common ones. Revealed: The most polluted suburbs in Australia. Environment, land and water. Interactive Air Quality Tutorial. Climate & Clean Air Coalition.
Columbia Public Health. Special Issue : Indoor Air Quality and Health Outcomes in Energy-Efficient Buildings. Special Issue : Air Quality Monitoring and Assessment for Enhanced Living Environments and Public Health. Special Issue : Air Pollution Impact on Children’s Health. Indoor Exposure to Selected Air Pollutants in the Home Environment: A Systematic Review. IFA - Practical aids: Indoor workplaces. Workers diagnosed with silicosis push for ban on engineered stone after National Dust Disease Taskforce report At least 27 people poisoned by carbon monoxide at illegal bunker rave in Norway. Indoor air - Home Page. Household air pollution. Gas stove cooking routinely generates unsafe levels of indoor air pollution. Eleven people leave hospital after carbon monoxide poisoning due to grill used inside home - ABC News.
Air Conditioning suspected to play major role in coronavirus spread. IFA - Practical aids: Indoor workplaces - Volatile organic compounds (VOC) Call to phase out wood heaters due to health, environmental concerns – but minister says move not supported by community. Healthy Homes for Renters. Melbourne communities urged not to drink tap water potentially contaminated after storms.
Victoria storms: Thousands of residents east of Melbourne told not to drink tap water. Melbourne suburbs served by Yarra Valley Water, South East Water warned to boil water after wild weather - ABC News. Australian Drinking Water Guidelines. Water Quality Home. Cultural and spiritual values. Indigenous cultural and spiritual values in water quality planning. Methods Approved to Analyze Drinking Water Samples to Ensure Compliance with Regulations. Is bottled water safer than tap water? Water filters: do you need one? - food and drink. Understanding The Deadly Salmonella Bacteria - Connect For Water. New EZ Coliform Cult – MUG Bacteria Test - Water Canada. Standard drinking water sampling technique microbiological. Table of Contents. Water. Publications and presentations Revitalising Informal Settlements and their Environments. Brain-eating microbe: US city warned over water supply. Home. NSW Food Authority. Food Act and Food Standards Code.
Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code - Standard 3.2.1 - Food Safety Programs (Australia Only) Manual keys. Contact tracing in the spotlight as experts warn of major animal disease risk. Natural Toxins in Food Plants. Causes and Symptoms of Foodborne Illness - Minnesota Dept. of Health. No cover Framework program tools final 41384.