

A Molecular Checkup: The Nano Future of Medicine. Not long ago cancer medicine in the U.S. passed a hopeful milestone: for the first time, the incidence rates for both new cases and deaths in men and women declined, according to an annual report issued in late November from the National Cancer Institute, the American Cancer Society and other leading organizations.
Search. Search. MIT Senseable City Lab's Seaswarm oil-absorbing nanotechnology: Scientific American Video. A Molecular Checkup: The Nano Future of Medicine. Nanotechnology and technology and innovation news from Scientific American. How far are we from realizing practical benefits from nanotechnology? This question is a tricky one because " nanotechnology " is such a broad and vague term.
Four researchers wrote in to give their views regarding the meaning of nanotechnology and when we will begin to benefit from it. James D. Plummer, professor of electrical engineering at Stanford University, replies: Government Fails to Assess Potential Dangers of Nanotechnology. Pesticide DDT, industrial lubricants PCBs and now plastic BPA (bisphenol A) are all widely used industrial chemical compounds that have been discovered to cause ills such as cancer and/or environmental damage.
Worried that the latest chemical craze—nanoparticles (molecules and even atoms engineered at the scale of one billionth of a meter or smaller)—may follow suit, a panel of scientists is urging federal government agencies to assess the potential risks posed by such engineered chemicals and particles before they are used in any more substances. The National Research Council, one of The National Academies in Washington, D.C., (scientific advisory bodies for the federal government) charges that the 18 government bodies, including the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) tasked with assessing chemical safety, have failed to prove that the diminutive particles are not dangerous. Preying On a Tumor's Weakness with Nanotechnology to Fight Cancer. The Harvard–M.I.T.
Division of Health Sciences and Technology (HST) today named Geoffrey von Maltzahn this year's recipient of the $30,000 Lemelson–M.I.T. Student Prize for developing a technique that utilizes nanosize gold particles to target malignant tumors and kill cancer cells but spares healthy tissue. Established in 1994, the award is given out annually to a Massachusetts Institute of Technology senior or graduate student who has contributed significantly to the fields of science or technology. Technology Timeline. This timeline features Premodern example of nanotechnology, as well as Modern Era discoveries and milestones in the field of nanotechnology.
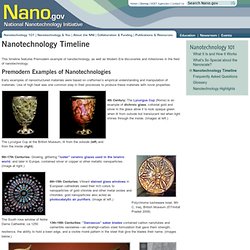
Early examples of nanostructured materials were based on craftsmen’s empirical understanding and manipulation of materials. Use of high heat was one common step in their processes to produce these materials with novel properties. 4th Century: The Lycurgus Cup (Rome) is an example of dichroic glass; colloidal gold and silver in the glass allow it to look opaque green when lit from outside but translucent red when light shines through the inside. (Images at left.) How Does Eating Healthy Affect Your Physical, Mental & Social Health? Food powers your life.
It fuels all bodily processes that enable you to move, think and breathe. There is no aspect of your life that is not influenced by what you eat. Fueling your body with processed food, fast food, sugar, fat and calorie-dense food affects who you are, what you do and your ability to pursue your dreams and aspirations.
Food is that powerful – use it to your advantage. Physical Well Being Strength, agility, coordination, endurance, speed and level of performance are all powered by the foods you eat. Mental Health Food supplies the source of power for your brain as well as your body, and has a direct relationship to mental and emotional health and stability. Eating and Relationships Eating a healthy diet keeps you physically and mentally fit. Healing, Fueling and Feeding the World. Polio Vaccine. Zuschkeimmunology.
This Day in History: Apr 26, 1954: Polio vaccine trials begin. What is Nanotechnology? Nanotechnology is science, engineering, and technology conducted at the nanoscale, which is about 1 to 100 nanometers.

Nanoscience and nanotechnology are the study and application of extremely small things and can be used across all the other science fields, such as chemistry, biology, physics, materials science, and engineering. Meg In Progress. Sun Plus Nanotechnology: Can Solar Energy Get Bigger by Thinking Small? Patrick J. Kiger Nearly 60 years after researchers first demonstrated a way to convert sunlight into energy, science is still grappling with a critical limitation of the solar photovoltaic cell. It just isn't that efficient at turning the tremendous power of the sun into electricity. And even though commercial solar cells today have double to four times the 6 percent efficiency of the one first unveiled in 1954 by Bell Laboratories in New Jersey , that hasn't been sufficient to push fossil fuel from its preeminent place in the world energy mix.
Westjmed00314-0057. Injectable Nanoparticles may Simplify Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes. Written by AZoNanoMay 16 2013 Nanotechnology could help fight diabetes.
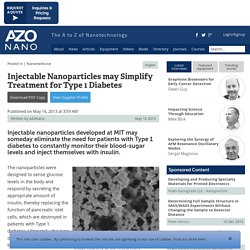
Image courtesy of the researchers The nanoparticles were designed to sense glucose levels in the body and respond by secreting the appropriate amount of insulin, thereby replacing the function of pancreatic islet cells, which are destroyed in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Ultimately, this type of system could ensure that blood-sugar levels remain balanced and improve patients’ quality of life, according to the researchers.